It is the assumption that the researcher is seeking to expose. It is designated as H-naught.
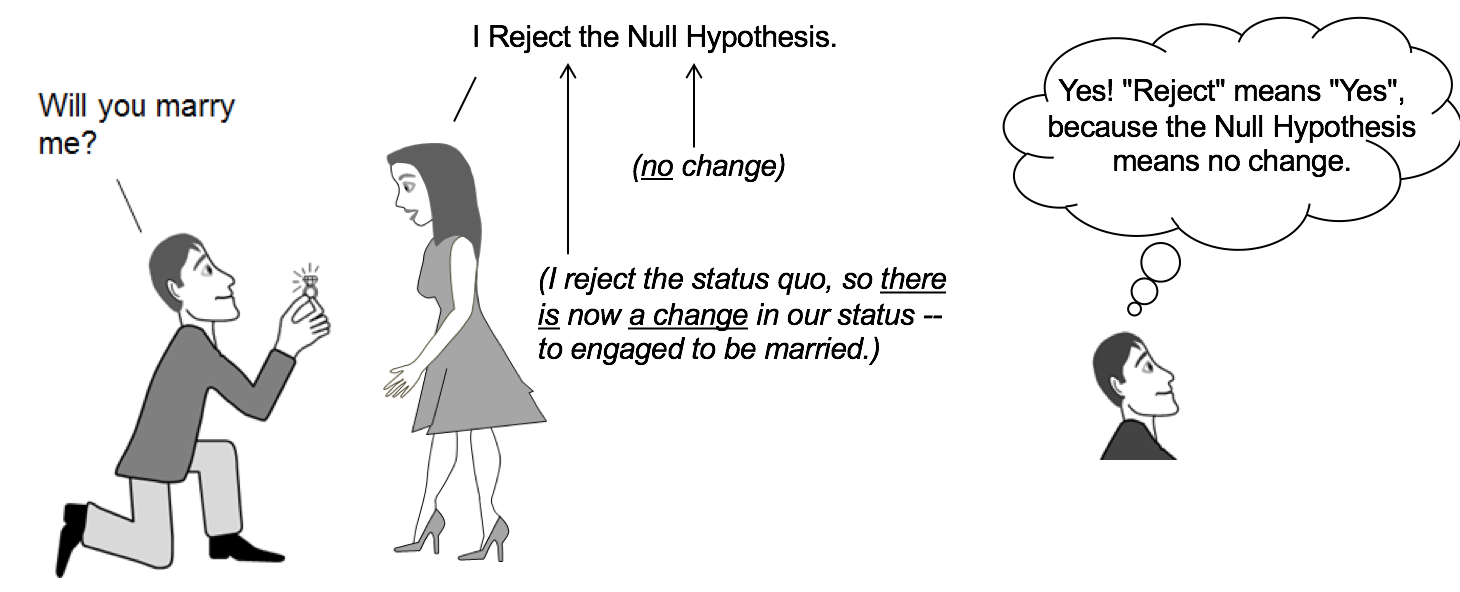 Challenge The Status Quo Using Hypothesis Testing In Statistics Part One By Shubham Singh Medium
Challenge The Status Quo Using Hypothesis Testing In Statistics Part One By Shubham Singh Medium
Thus it negates the researchers perception or assumption.

What is a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is what we attempt to find evidence against in our hypothesis test. If either requirement can be positively overturned. If the null hypothesis is true any observed difference in phenomena or populations would be due to sampling error random chance or experimental error.
If our p-value is greater than alpha then we fail to reject the null hypothesis. It is always the hypothesis that is tested. The null often refers to the common view of something while the alternative hypothesis is what the researcher really thinks is the cause of a phenomenon.
Null Hypothesis - Definition Symbol Formula Types and Examples The null hypothesis is a hypothesis in which the sample observation results from chance. A null hypothesis is a type of hypothesis used in statistics that proposes that there is no difference between certain characteristics of a population or data-generating process. For example a null hypothesis statement can be the rate of plant growth is not affected by sunlight.
Null hypothesis definition is - a statistical hypothesis to be tested and accepted or rejected in favor of an alternative. The null hypothesis is effectively stating that a quantity being larger or equal to zero AND smaller or equal to zero. A null hypothesis is a theory based on insufficient evidence that requires further testing to prove whether the observed data is true or false.
We hope to obtain a small enough p-value that it is lower than our level of significance alpha and we are justified in rejecting the null hypothesis. As it is a weak prediction ie. Th th 0.
For example there is no statistically meaningful relationship between the type of water fed to the plants and growth of the plants. Typically the quantity to be measured is the difference between two situations for instance to try to determine if there is a positive proof that an effect has occurred or that samples derive from different batches. In hypothesis testing there is a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
The null hypothesis H 0 is a hypothesis which the researcher tries to disprove reject or nullify. Null hypothesis presumes that the sampled data and the population data have no difference or in simple words it presumes that the claim made by the person on the data or population is the absolute truth and is always right. The hypothesis that an observed difference as between the means of two samples is due to chance alone and not due to a systematic cause.
The idea is to develop a test statistic that has a known distribution under the null hypothesis and see if the observed value of the test statistic based on the data is unusual when compared against this known distribution. In a scientific experiment the null hypothesis is the proposition that there is no effect or no relationship between phenomena or populations. We can define null hypothesis as a general statement or a default position that says there is no relationship between two measured phenomena or there is no association among groups.
It is usually the hypothesis a researcher or experimenter will try to disprove or. Null Hypothesis H 0. A null hypothesis is a foundation of the scientific method as scientists use experiments to accept or reject a null hypothesis based upon the relationship or lack thereof between two phenomena.
It is usually the hypothesis a researcher or experimenter will try to disprove or discredit. It denotes the certain value of population parameter such as µ s p. A null hypothesis is an initial statement claiming that there is no relationship between two measured events.
A null hypothesis is a hypothesis that says there is no statistical significance between the two variables. It is the original or default statement with no effect often represented by H 0 H-zero. The null hypothesis is something to which the researcher aims to find evidence against its perception.
In statistics null hypothesis is denoted H0 and is pronounced as H-nought or H-null or H-zero with the subscript being the digit equal to 0. An experiment conclusion always refers to the null rejecting or accepting H 0 rather. In inferential statistics the null hypothesis is a default hypothesis that a quantity to be measured is zero.
A null hypothesis is a statistical hypothesis in which there is no significant difference exist between the set of variables. Null Hypothesis in Statistics A null hypothesis is a theory that assumes there is no statistical importance between the two variables in the hypothesis. Though the researcher is not able to find evidence in support of their claim still the existence of the negation is just a matter of chance.
A null hypothesis states there is no statistical significance between the two variables tested. Learn the definition principles and types of the null hypothesis at BYJUS.
 The Confusion Matrix Of Accepting Or Rejecting The Null Hypothesis H0 Download Scientific Diagram
The Confusion Matrix Of Accepting Or Rejecting The Null Hypothesis H0 Download Scientific Diagram
 Examples Of Null And Alternative Hypotheses Video Khan Academy
Examples Of Null And Alternative Hypotheses Video Khan Academy
 What Role Does The Null Hypothesis Really Play In The Scientific Process Dsm1lp
What Role Does The Null Hypothesis Really Play In The Scientific Process Dsm1lp
 Pin On Educ388t Inquiry Sessions
Pin On Educ388t Inquiry Sessions
 Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis Explained In 2020 Learn Data Science Today
Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis Explained In 2020 Learn Data Science Today
 Null Hypothesis Null Hypothesis Research Methods Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Null Hypothesis Research Methods Hypothesis
 Hypothesis Testing Null And Alternative Hypotheses Youtube
Hypothesis Testing Null And Alternative Hypotheses Youtube
/null-hypothesis-examples-609097_FINAL-100262e70b70426fb0633304eb2f49f4.png) Examples Of The Null Hypothesis
Examples Of The Null Hypothesis
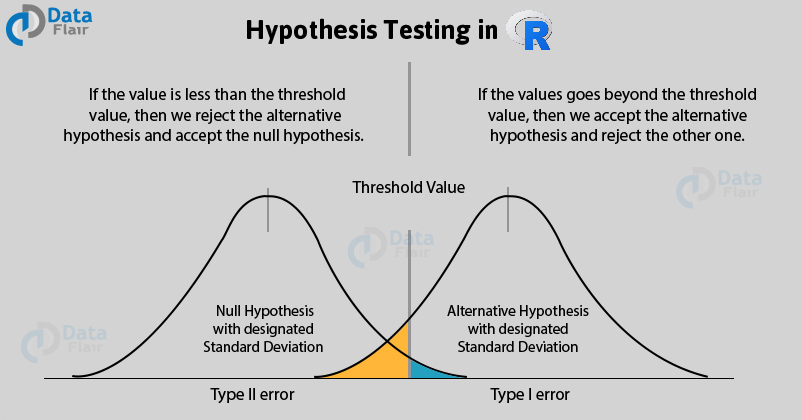 Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
 Difference Between Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis With Simple Example Youtube
Difference Between Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis With Simple Example Youtube



/null-hypothesis-vs-alternative-hypothesis-3126413-v31-5b69a6a246e0fb0025549966.png)