The pH of an aqueous of the corresponding salt B A will be. Weak electrolytes do not.
 Acids And Bases Ph And Titrations Ppt Video Online Download
Acids And Bases Ph And Titrations Ppt Video Online Download
BaOH2 barium hydroxide.
H2so4 strong or weak. H2SO4 sulfuric acid. Strong electrolyte soluble and strong acid Chloric acid. In your first list H2SO4 is usually defined as strong but the ionization is two part.
When the strong acid has been completely. Identify each acid or base as strong or weak. Instructions For Electrolytic Behavior Table Light.
HSO4- already has a negative charge so its much harder to pull of an H. Account for the difference in strength of these two related species. The acids corrosiveness towards other.
MgOH 2 C 5 H 5 N. In this curve there are two break points. Indicate If The Substance Is A Strong Electrolyte Weak Electrolyte Or Non-electrolyte Substances Present In Solution.
Strong dehydrating acids H2SO4 H3PO4 favor elimination dehydration in alcohols. Because they are strong acids they readily protonate the alcohol thereby converting a poor leaving group OH- into a good leaving group HOH however the anions produced after protonation of the alcohol HSO4- or H2PO4- are very poor nucleophiles and can. H2SO4 H HSO4-.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound CaBr2. Hydrofluoric acid while a weak acid would pass through your hand and attack your bones. Sulfuric acid American IUPAC spelling or sulphuric acid traditional British spelling also known as oil of vitriol is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur oxygen and hydrogen with molecular formula H 2 SO 4It is a colourless and viscous liquid that is soluble in water and is synthesized in reactions that are highly exothermic.
HSO4- H SO4 but even without extra water it goes 95. Indicate If The Bulb Brightness Is Bright Dim Or No Light Observed Electrolyte. Therefore we refer to H2SO4 as a strong acid BUT only for the first proton that is released.
The HSO4- ion is a weak acid and only partially dissociates. For H2SO4 the proton leaves a neutral molecule. For that reason a 1 M solution of H2SO4 will NOT produce a 2M hydrogen ion concentration but instead it will produce just a little over 1 M hydrogen ions.
Conductometric titration of a weak acid acetic acid vs. - Hydrochloric Acid HCl - Hydrobromic Acid HBr - Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 - Perchloric Acid HClO4 - Nitric Acid HNO3 - Hydroiodic Acid HI - Periodic Acid HIO4 - Chloric Acid HClO4 Strong Bases. The second ionization may not go 100 unless extra water is used.
Because MgOH 2 is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong base. HNO2 nitrous acid. A Strong Base or a Weak Base.
The p K b of a weak base B O H is 4. Strong Weak And Nonelectrolytes. ACID BASE HCI CI- H2SO4 HSO4- - Negligible Strong- HNO3 NO3- H30 H20 HSO4 so2- H2SO3 HSO3- H3PO4 H2PO4 HF F- CH3COOH CH3CO0- H2CO3 HCO- Weak H2S HS- Weak- HSO3- SO32- H2PO4- HPO42- HCN CN- NH4 NH3 HCO3- Co22- HPO42- PO43- H20 On- HS- S2- Strong Negligible - On- 02- ACID STRENGTH BA SE STRENGTH.
H2SO4 is a strong acid but HSO4- is a weak acid. CH3COOH acetic acid. Strong electrolyte strong acid H2SO4.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound AlCl3. Tell What Substance Is Dissolved. HI hydroiodic acid.
Answer to H2SO4 is a strong acid but is a weak acid. Mixture of a Strong Acid and a Weak Acid vs. HF hydrofluoric acid.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound Perchloric acid. Account for the difference in strength of these two related species. Because HCl is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong acid.
HCN hydrocyanic acid. - Sodium Hydroxide NaOH. While acids tend to be corrosive the strongest superacids carboranes are actually not corrosive and could be held in your hand.
HCOOH formic acid. The first break point corresponds to the neutralization of strong acid. HBr hydrobromic acid.
The nitrogen in C 5 H 5 N would act as a proton acceptor and therefore can be considered a base but because it does not. The dissociation constant of two acids H A 1. Strong electrolyte strong acid Potassium hydroxide.
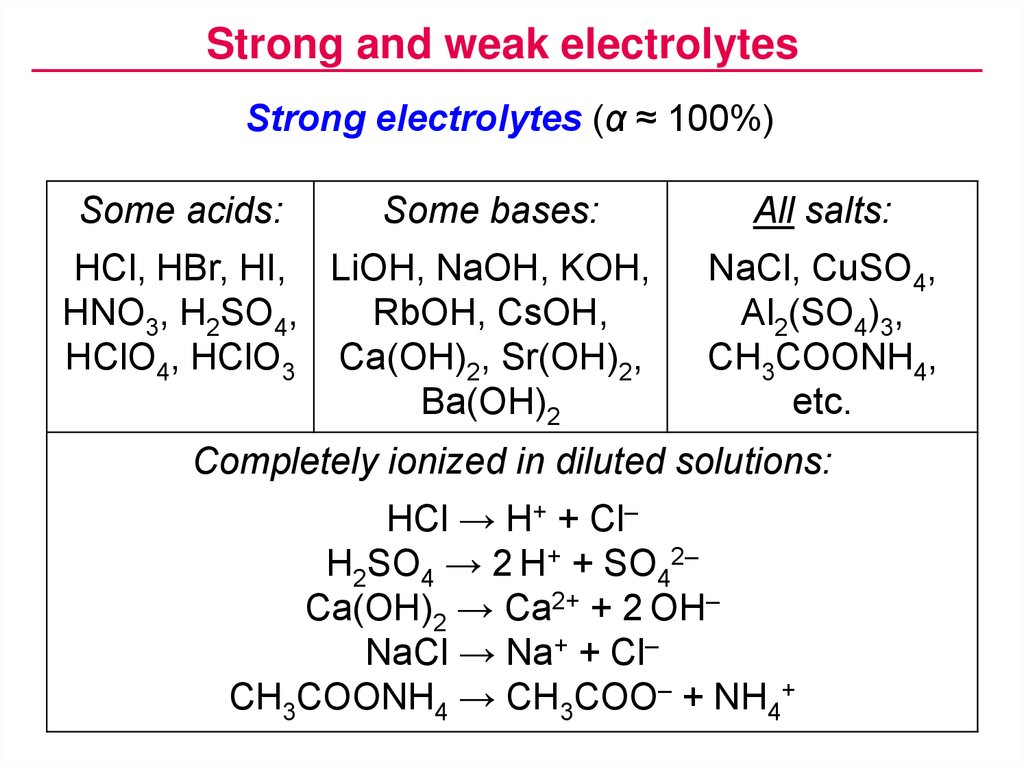
A strong acid or base is one that is completely ionized in a solution. Strong electrolytes ionize completely upon solvation. H2SO4 is a strong acid.
1 H2SO4 -- H HSO4-The remaining bisulfate ion HSO4- is a weak acid and only partially dissociates. A weak base NH 4OH 5. Choose strong acids from the following CH3COOH H2SO4HNO3H2CO3 - 5429451.
The reason is that sulfuric acid is highly corrosive while acetic acid is not as active. Strong electrolyte soluble and strong acid HNO3. Follow up.
It is a strong acid only for the first hydrogen ion that is produced.
Thus we see more oxygen atoms means more possible strutures which means stronger the acid. The answer is b.
 In Aqueous Solution Classify These Compou Clutch Prep
In Aqueous Solution Classify These Compou Clutch Prep
While acids tend to be corrosive the strongest superacids carboranes are actually not corrosive and could be held in your hand.
H3po4 strong or weak. A strong acid is one that nearly completely dissociates. Because H3BO3 is a. Classify The Compounds As A Strong Acid Weak Acid Strong Base Or Weak Base.
Strong dehydrating acids H2SO4 H3PO4 favor elimination dehydration in alcohols. H3PO4 is a weak acid and a weak acid is not sufficient for a buffer. Along with the higher electronegativity of N relative to P the extra oxygen makes HNO3 a strong acid while the lack thereof makes H3PO4 weak.
H2S HS-Weak Acid Weak Base. Any base not listed is a weak base. H3PO4 H2PO4-Weak Acid Weak Base.
The chloride ion is incapable of accepting the H ion and becoming HCl again. HClO2 is a weak acid and HClO is even weaker. Why the conductivity of H3BO3 is lower than H3PO4 while they each free the same amount of ions per mole.
Phosphoric acid also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric V acid is a weak acid with the chemical formula H 3 P O 4. H2CO3 HCO3-Weak Acid Weak Base. A strong base is a base that is 100 ionized in solution.
While phosphoric acid is quite acidic it is evident that it is indeed a weak acid because of the lack of full dissociation in water. Weak Acids weak electrolytes If the acid is not one of the strong acids above you can safely assume its a weak acid. The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of phosphoric acid is 69x10³.
The issue is similar with bases. HC2H3O2 C2H3O2-Weak Acid Weak Base. It readily gives up one two and then three H ions in solution and is therefore a strong acid.
It is normally encountered as a colorless syrup of 85 concentration in water. Weak acids are defined as such based on the value of th. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
The definition of weak acid is acid that ionises partially in water to produce hydrogen ion H. The reason is that sulfuric acid is highly corrosive while acetic acid is not as active. HF F-Weak Acid Weak Base.
The general rule is that the acid is stronger if it has more O atoms in a series such as this. Start studying Strong and Weak Acids and Bases. HClO4 H C l O 4 Strong acids are acids that dissociate completely when they are dissolved in water forming hydronium ions and the corresponding anion.
All strong bases are OH compounds. A weak acid does not dissociate much at all. HSO3-SO32-Weak Acid Weak Base.
Is h3po4 a strong or weak acid. A 1 M solution of strong acid would be around 0 0 for monoprotic species possibly less for diprotic due to an additional hydrogen ion. HClO4 perchloric acid is a very strong acid as is HClO3.
HSO4-SO42-Weak Acid Weak Base. If it is less than 100 ionized in solution it is a weak base. Strong Acid Weak Base.
Strong Acid Weak Acid Strong Base Weak Base Answer Bank H2CO3 KOH NH3 HBr H3PO4 HSO4 BaOH2. After H3PO4 does lose a proton it forms H2PO4- which lacks sufficient resonance stabilization. After H3PO4 does loose a proton it forms H2PO4- which lacks sufficient resonance stabilization.
In general the stronger the acid the weaker its conjugate base. Like the strong acid reactions given above each reaction has water as a reactant and the H is donated to it to form H 3O. There are very few strong bases Table 1471.
Hydrofluoric acid while a weak acid would pass through your hand and attack your bones. In order for H3PO4 to be a strong acid a proton must be able to easily fall off Along with the higher electronegativity of N relative to P the extra oxygen makes HNO3 a strong acid while the lack there of makes H3PO4 weak. Because HCl is a strong acid its conjugate base Cl is extremely weak.
H2SO3 HSO3-Weak Acid Weak Base. As I know H3PO4 is a mineral salt and ionises completely in water to produce H. Likewise the weaker the acid the stronger its conjugate base.
Because they are strong acids they readily protonate the alcohol thereby converting a poor leaving group OH- into a good leaving group HOH however the anions produced after protonation of the alcohol HSO4- or H2PO4- are very poor nucleophiles and cant replace the leaving group. EXAMPLES FROM NOMENCLATURE THAT YOU NEED TO MEMORIZE-HNO 2 Nitrous Acid HNO 2 W H NO. H3PO4 is phosphoric acid.
The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get weaker as we move to the top of the table. The ChemTeam will try to use several different weak acids in the examples to follow.
/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png) List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids
List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids
Nitric acid HNO 3.
List of weak acids and bases. As a result they are commonly found in various household applications especially as cleaners and in the kitchen. CaOH 2 - calcium hydroxide. H 2 CO 3.
Furthermore weak acids and bases are very common and we encounter them often both in the academic problems and in everyday life. The time honored example weak acid is acetic acid. Acetic acid also known as ethanoic acid is a weak acid with the chemical formula CH 3 COOH.
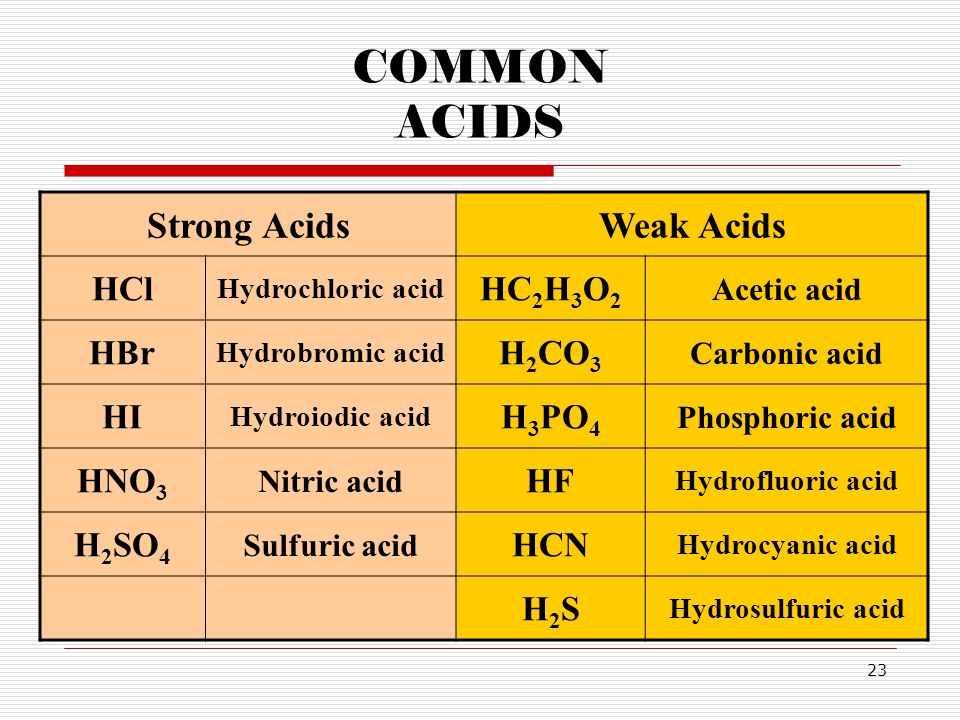
Acetic acid is a weak acid because it only partially dissociates into its constituent ions when dissolved in water. There are very few strong bases Table PageIndex1. The strong acids are hydrochloric acid nitric acid sulfuric acid hydrobromic acid hydroiodic acid perchloric acid and chloric acid.
TextHF is a weak acid. The nitrogen in C 5 H 5 N would act as a proton acceptor and therefore can be considered a base but because it does not. Common Strong Bases Weak Bases Strong Acids and Polyprotic Acids.
Various common acids and bases that you should memorize. Weak acids and bases are only partially ionized in their solutions whereas strong acids and bases are completely ionized when dissolved in water. If it is less than 100 ionized in solution it is a weak base.
Weak bases do not furnish OH - ions by dissociation. N ext comes acetic acid a primary constituent of vinegar. RbOH - rubidium hydroxide.
It is known to be the active component of vinegar which is a 4 7 solution of acetic acid in water. CH 3 COOH H 2 CO 3. Strong acids are listed at the top left hand corner of the table and have Ka values 1 2.
Complete List of Acids Complete List of Bases Molar to Mass Concentration Converter Molar Mass Calculator Cations Anions List Dilution Calculator Molarity Calculator Compound Prefixes Water Insoluble Compounds Compound Quiz Concentration Solution Unit Converter English Word Search. When you combine acids and bases into a mixture they neutralize each other. HCl HNO 3 H 2 SO 4.
FEEL FREE TO EDIT OR ADD MORE TO THE SET. Strong and Weak Bases. An acid is a compound that dissolves in water to release hydrogen ions.
NH 3 CH 3 CH 2 NH 2. CsOH - cesium hydroxide. Bases are also molecules that are bitter in taste and have opaque coloring.
Weak acids and bases. The issue is similar with bases. The most common example among weak bases is ammonia NH 3.
BaOH 2 - barium hydroxide. - poor conductors - low value for current passing. Acids are molecules that release hydrogen ions or protons in a solution.
- good conductors Weak bases. H 3 PO 4. Acids and bases are generally chemically active in that they can react with many other substances.
Terms in this set 25 HCl hydrochloric acid strong acid. Examples of weak bases include ammonia NH 3 and diethylamine CH 3 CH 2 2 NH. They are generally sour and can dissolve metals.
Group 1 hydroxides ie NaOH etc or lower group 2 hydroxides BaOH 2. In fact it has its own abbreviation of HAc where H means hydrogen and Ac means acetate. All strong bases are OH compounds.
Weak acid and weak base A weak acid or base is one where only a small percentage of molecules dissociate to form ions in solution. - good conductors - large value for current passing. Because HCl is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong acid.
SrOH 2 - strontium hydroxide. The only weak acid formed by the reaction between hydrogen and a halogen is hydrofluoric acid HF. A weak acid or base is one where only a small percentage of molecules will dissociate to form ions in solution.
Identify each acid or base as strong or weak. Acetic acid being a weak acid when released into the air is broken down naturally by sunlight. The reason for this is that strong acids and bases are 100.
Weak acid - an acid that only partly ionizes in water producing hydrogen ions. MgOH 2 C 5 H 5 N. C5H5N pyridine Remember any base that dissolves in water is an alkali and must have a pH above 7.
Acids and bases are either strong or weak. It has many uses ranging from manufacturing inland dyes pesticides food preservatives rubber plastic and many more. A strong base is a base that is 100 ionized in solution.
Like weak acids weak bases do not completely dissociate in aqueous solution. Weak Acids - Tylenol acetaminophen K a - 12 x 10 -10 and Aspirin acetylsalicylic acid or ASA K a - 327 x 10 -4. Any base not listed is a weak base.
Because MgOH 2 is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong base. Acid with values less than one are considered weak. Also we run into a bit of a technicality in the language.
Strong acids - hydrochloric acid HCl. Some common weak acids and bases are given here. Diethylamine CH 3 CH 2 2 NH.
Most weak bases are anions of weak acids. CH 3 NH 2.
This equation shows that the pH of a solution of a weak acid depends on both its K a value and its concentration. We know that this acid is weak since its acid dissociation constant K a is given.
 Iterative Method For Calculating Ph Of A Weak Acid Base Chemistry Stack Exchange
Iterative Method For Calculating Ph Of A Weak Acid Base Chemistry Stack Exchange
The strongest acids like HCl and H 2 SO 4 have K a values which are too large to measure while another strong acid HNO 3 has K a value close to 20 molL.

Ph of weak acid. The procedure for calculating the pH of a solution of a weak base is similar to that of the weak acid in the sample problem. Again there are exceptions to this general pH range. The pH of a 200 M solution of a strong acid would be equal to log 200 030.
Ethanoic acid is an example of a weak acid in 1 mol dm-3 solution only about 4 in every thousand ethanoic acid molecules are dissociated into ions and therefore the degree of dissociation is 41000. Most organic acids are weak acids. Here is a partial list ordered from strongest to weakest.
Use Ka to determin. Examples include acetic acid CH 3 COOH the main component of vinegar and formic acid HCOOH the acid responsible for the sting of ant bites. An acid such as oxalic acid HOOCCOOH is said to be dibasic because it can lose two protons and react with two molecules of a simple base.
Weak acids do not completely dissociate into their ions in water. We can write down the dissociation of the acid via the ICE table. Note there are exceptions.
Now to answer how to calculate the pH of a weak acid put these values in the pH equation which can be expressed as pH - log H Therefore we can write pH - log x pH - log 806 x 10-4 Therefore pH - -309 309. Note that strong acids are fully dissociated hence do not have K a values. As an example if weak acid concentration is 01 mol dm -3 H 3 O concentration may be 00001 mol dm -3.
That solution pH is 4. The lower the pH the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. The higher pH of the 200 M nitrous acid is consistent with it being a weak acid and therefore not as acidic as a strong acid would be.
Acids like the ammonium ion NH 4 and hydrogen cyanide HCN for which K a is. In a 0100 M aqueous solution lactic acid is 37 dissociated. Salts of weak acids and weak bases WA-WB Let us consider ammonium acetate CH 3 COONH 4 for our discussionBoth NH 4 ions and CH 3 COO-ions react respectively with OH-and H ions furnished by water to form NH 4 OH weak base and CH 3 COOH acetic acid.
Let BA represents such a salt. In this JC2 webinar we want to learn how to calculate the pH of a weak acid. Strong acids like hydrochloric acid at the sort of concentrations you normally use in the lab have a pH around 0 to 1.
A weak acid on the other hand fails to ionize completely. The pH value of a solution can go lower than 0 and greater than 14 in the case of really strong acids and bases. More free chemistry help videos.
PH 684 and an initial acid concentration of 143 x 10 M note. PH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. Typical examples of weak acids include acetic acid and phosphorous acid.
Pure water is neutral at 25 C and has the standard neutral pH value of 7. Weak acids do not ionise fully in a solution and therefore the H is not proportional to the acid concentration. Acids are solutions with a pH value less than 7 whereas bases are solutions with a pH value greater than 7.
Lactic acid HC 3 H 5 O 3 is a waste product that accumulates in muscle tissue during exertion leading to pain and a feeling of fatigue. For example HF dissociates into the H and F-ions in water but some HF remains in solution so it is not a strong acid. For More Chemistry Formulas just check out main pahe of Chemsitry Formulas.
Calculate the pH of a solution of a weak monoprotic weak acid or base employing the five-percent rule to determine if the approximation 2-4 is justified. Lets take a look at this question. If there are two solution one is a weak acid and other one is a strong acid.
Typical weak acids such as HF and CH 3 COOH have acid constants with a value of 10 4 or 10 5 molL. Determination of the pH of a weak base is very similar to the determination of the pH of a weak acid. This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the pH of weak acids and bases such as HC2H3O2 and NH3 given Ka acid dissociation constant and Kb.
There are many more weak acids than strong acids. It releases fairly low concentrations of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution resulting in a pH range of about 5 to just below 7. The pH of a weak acid should be less than 7 not neutral and its usually less than the value for a strong acid.
Solution for Please calculate the Ka for a weak acid given the following data. This is a rather simpler method for calculating the pH of the weak acid. Predict whether an aqueous solution of a salt will be acidic or alkaline and explain why by writing an appropriate equation.
If both of them concentration are same pH of weak acid is higher than strong acid. Calculate the value of K a for this acid. For example the pH of hydrochloric acid is 301 for a 1 mM solution while the pH of hydrofluoric acid is also low with a value of 327 for a 1 mM solution.