Become a member and. It helps in transpiration and removal of excess water in the form of water vapour.
Their primary function is to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
/plant-stomata-function-4126012-01-025d7d9b984d46c2b9f9ab5290d25838.png)
What is the purpose of stomata. Different factors can affect its shape and size effectively regulating water uptake transport and the distribution of nutrients and hormonal signals in the different organs of plants thus controlling growth. Click card to see definition. In many plants stomata remain open during the day and closed at night.
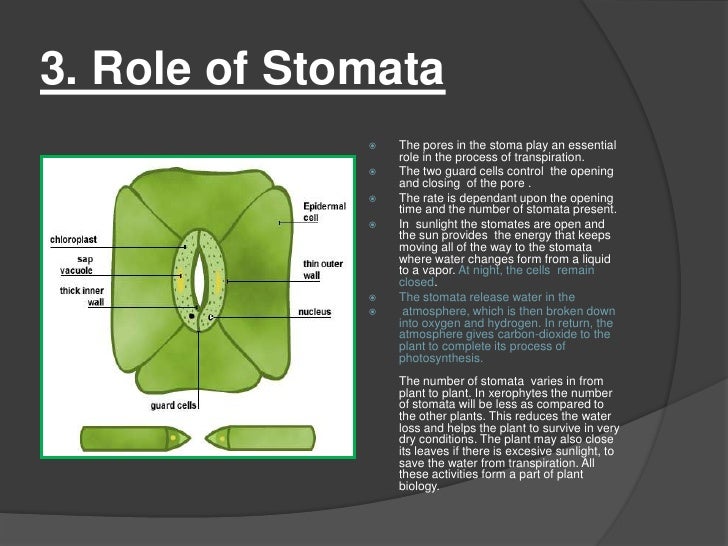
Control gas exchange in the leaf. Control water lost by transpiration. Stomatal closure at night prevents water from escaping through pores.
They are organs that absorb CO2 releasing oxygen and water. The stomata can open and close to. The main functions of stomata are.
Stomata are akin to pores in the skin on the underside of a land-based plant leaf. The harvested carbon dioxide is converted into fuel to feed cell production and other important physiological processes. 1 at night stomatas closed and guard cells lay flat against each other.
Stomata are open during the day because this is when photosynthesis typically occurs. Stomata of fossil plants can be used to directly estimate past carbon dioxide levels and those carbon dioxide levels can then be used to make an indirect estimate of temperature. Tap card to see definition.
Stomata are the door and windows of the leaves. The stomata are pours that plants use to increase gas exchange. The stomata are located on the outer leaf skin layer.
A group of 4 police officers have body cams one What is the purpose of a stomata Published by Rodrigo Anthony. They provide for the exchange of gases between the outside air and the air canals within the leaf. Once inside these air spaces the CO 2 can be used by the plants photosynthetic tissues as sources of carbon to build sugars amino acids and more.
Typically although there are exceptions to the rule fossils with many stomata low carbon dioxide came from times of low global temperature and fossils with few stomata high carbon dioxide came from times of high global temperatures. The primary stomata function is to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen this is done with the assistance of guard cells which voluntarily open and close the pore for the exchange of gases. Opening and closing of stomata.
The term is usually used collectively to refer to. Where is the stomata. Sunken stomata are commonly found in plants in arid environments as one of their adaptations to preserve water.
A sunken stomata is a stomata in a small pit which protects the escaping water vapor from air currents decreasing water loss from the leaf. Ideally it is best for stomata to absorb as much CO2 as possible to facilitate photosynthesis. Learn more about stomata and the guard cells that regulate their opening and closing.
While transpiration is an important function of stomata the gathering of CO2 is also vital to plant health. The stomatas main purpose is to let gases like oxygen and water vapor pass through. On the other hand if the stomata remain open for too long the plant will suffer from a loss of moisture.
In summary stomata play a vital role in plant development by regulating gas exchange with the atmosphere and controlling transpiration. In botany a stoma plural stomata also called a stomate plural stomates is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves stems and other organs that controls the rate of gas exchangeThe pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening. Stomate any of the microscopic openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems.
Opens when turgid pressure in guard cells is high and closes when low. Tiny openings called stomata allow plants to exchange gases necessary for cellular processes such as photosynthesis. The two main functions of stomata are to allow for the uptake of carbon dioxide and to limit the loss of water due to evaporation.
See full answer below. The technical term for this gas exchange and water exchange is transpiration. The process involving gas and water exchange is called transpiration.
The stomata open and close to allow this gas exchange. Each stoma can be open or closed depending on how turgid. During transpiration the stoma are off-gassing the waste by-product of photosynthesis oxygen.
3 space is created allowing gases and water molecules to move in and out of leaf. Sometimesurpose of is to keep the plant alivsearch for them in the woods. Plants have to balance how much time that their stomata remain in the open position.
Gaseous exchange- Stomatal opening and closure help in the gaseous exchange between the plant and surrounding. The primary purpose of stoma is to allow carbon dioxide gas to enter the air spaces in a plants tissues.