Elektron merupakan partikel subatomik lalu dari hal tersebut Thomson berhipotesis. Plum Pudding Atomic Theory.
 J J Thomson Atomic Model Ppt Video Online Download
J J Thomson Atomic Model Ppt Video Online Download
Thomson proposed that the shape of an atom resembles that of a sphere having a radius of the order of 10-10 m.

Jj thomson atomic theory. Thomson knew that the atom had positively and negatively. In Thomsons model the atom is composed of electrons which Thomson still called corpuscles. Through his work Thomson disproved the idea that atoms are indivisible.
Thomson discovered the electron by experimenting with a Crookes or cathode ray tube. Thomson yang menemukan bahwa aliran tersebut ini dibelokkan ke arah plat kutub positif. Thomson who discovered the electron in 1897 proposed the plum pudding model of the atom in 1904 before the discovery of the atomic nucleus in order to include the electron in the atomic model.
Thomsons Atomic Model also called as Plum Pudding Model was the most accepted Atomic Model during the year 1904-1910 which emphasized on the inner structure of the Atom. This post will discuss what is Thomsons Atomic Model postulates of JJ. JJ Thomsons Atomic Model and Theory.
Thomson membuktikan bahwa aliran tersebut terbentuk dari partikel kecil dari atom dan juga partikel tersebut bermuatan negatiflalu kemudian JJ. Thomson discovered the first subatomic particle the electron and his new model in 1897. Instead they are made of even smaller particles.
Thomson seorang fisikawan yang berasal dari inggris yang menemukan elektron suatu partikel bermuatna negatif yang lebih ringan daripada atom di tahun 1897. Thomson 1904 On the Structure of the Atom. It was strongly supported by Sir Joseph Thomson who had discovered the electron earlier.
The atomic theory of JJ Thomson is not only beneficial for atomic study but also other fields including the invention of mass spectograph. Home Timeline Atomic Theory Chemists Pictures. Thomson English physicist who helped revolutionize the knowledge of atomic structure by his discovery of the electron 1897.
Thomsons experiments with cathode rays led him to discover the electron the atoms negatively charged particle. Models In 1897 JJ. Thomson 1856-1940 was the first to offer evidence from scientific experimentation showing that the atom was not the basic and indivisible unit of matter it was previously thought to be.
Thomson also contributed to the discovery of the isotope and the atoms of the same element with different atomic weights. Thomson proposed his model of the atom in 1903then only electrons and protons were known to be present in the atom. This model explained the description of an inner structure of the atom theoretically.
In addition he also studied positively charged particles in neon gas. Thomsons Model How does Plum Pudding Model Work applications and limitations. His father was a bookseller who planned for Thomson to be an engineer.
He demonstrated that cathode rays were negatively charged. Thomson lived at a time when experimentation with charged particles was uncovering a lot about the secrets of atoms. He is one of the most influential people in the atomic study.
This article will cover atomic theory by JJ Thomson his early life and other atomic theories after his discovery. An Investigation of the Stability and Periods of Oscillation of a number of Corpuscles arranged at equal intervals around the Circumference of a Circle. The British physicist JJ.
He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1906 and was knighted two years later. During cathode ray tube experiment a negatively charged particle was discovered by JJ. Thomson Model of an atom.
Here is a brief biography of Thomson and interesting facts about his atomic theory. Thomsons atomic atomic model was called the Plum Pudding Atomic Model and it was based on the idea that electrons are negatively charged particles scattered through out the positively charged atom. Thomson atomic model was proposed by William Thomson in the year 1900.
Pengertian Kelebihan Kelemahan Contoh Gambar Kimia Ciri-Ciri Joseph John Thomson atau JJ. Learn more about his life career and legacy. Joseph John Thomson who was always called JJ was born in Cheetham Hill England near Manchester in 1856.
He specifically discovered the existence of a negatively charged particle called the electron. Thomson was the first scientist to propose a model for structure of an atom. Thomson an English scientist proposed the famous Thomson atomic model in the year 1898 just after the discovery of electrons.
With Application of the Results to the Theory of Atomic Structure Philosophical Magazine Series 6 Volume 7 Number 39 pp. Powered by Create your own unique website with customizable templates. There are also no protons and neutrons in this model.
While Thomson was right about the existence of electrons he was wrong on where they are located within the atom. Thomson atomic model earliest theoretical description of the inner structure of atoms proposed about 1900 by William Thomson Lord Kelvin and strongly supported by Sir Joseph John Thomson who had discovered 1897 the electron a negatively charged part of every atomThough several alternative models were advanced in the 1900s by Kelvin and others Thomson held that atoms are uniform. Thomson is the scientist who discovered the electron.
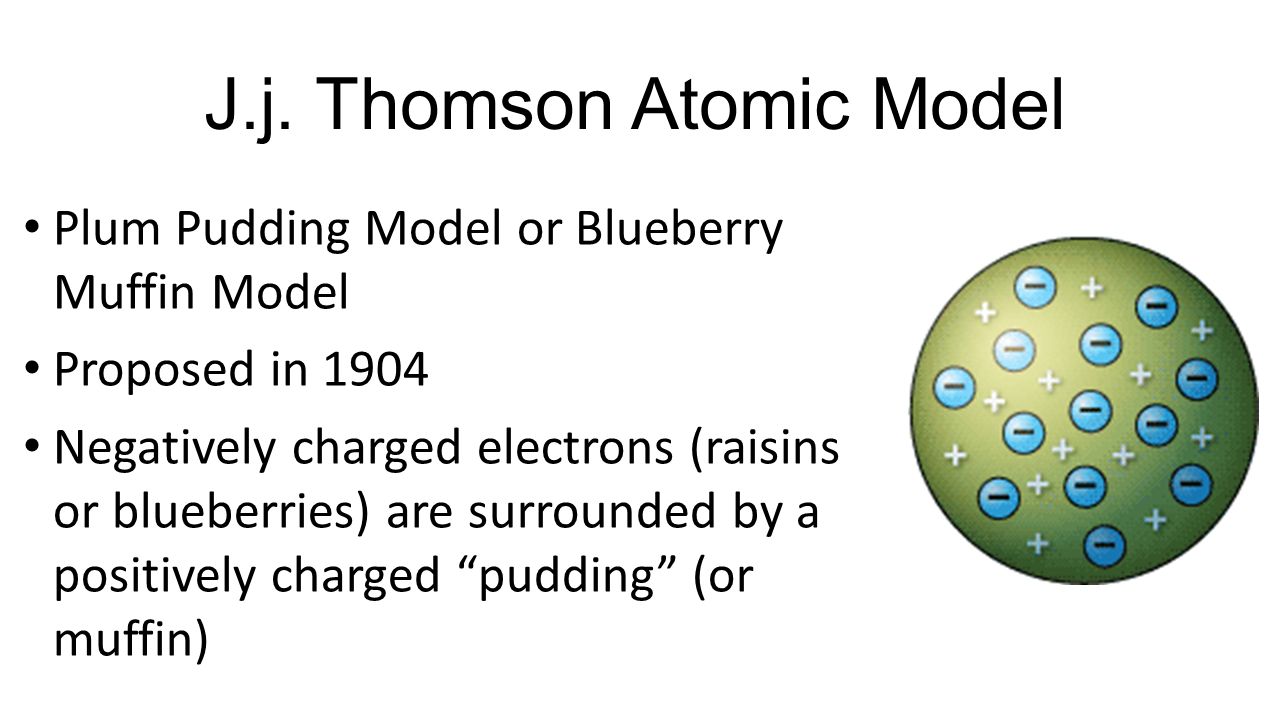
Thomson menamakannya dengan elektron. Karena elektron bermuatan negatif. JJ Thomson called his atomic model the Plum Pudding model because the electrons reminded him of plums surronded by pudding positive areas.
This model showed the atom having no structure. Thomsons model showed the atom as a positively charged ball of matter with negatively chaged electrons floating freely around inside of it.
He also found the first evidence that stable elements can exist as isotopes and invented one of the most powerful tools in analytical chemistry - the mass spectrometer. During cathode ray tube experiment a negatively charged particle was discovered by JJ.
 Thomson Atomic Model Description Image Britannica
Thomson Atomic Model Description Image Britannica
Learn more about his life career and legacy.
Jj thomson contribution to atomic theory. Thomsons experiments with cathode ray tubes showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles or electrons. JJ Thomson proposed the neutrality in the atom. It was strongly supported by Sir Joseph Thomson who had discovered the electron earlier.
Although a mathematician and an experimental physicist by training J. Thomsons greatest contribution to the Atomic Theory was the discovery of the existence of electrons. Thomson atomic model was proposed by William Thomson in the year 1900.
Known best for his substantial contributions to quantum theory and his Nobel prize winning research on the structure of atoms. Using this tool he discovered electrons which are small particles with a negative electric charge. Millikan and Thomsons Contributions to the Atomic Theory Theory Inferences From his experiments Thomson discovered that cathode rays were 1000 times lighter than hydrogen atoms and that the rays were always the same mass regardless of what atom it came from.
Thomson published an important monograph in 1913 urging the use of the mass spectrograph in chemical analysis. With Application of the Results to the Theory of Atomic Structure Philosophical Magazine Series 6 Volume 7 Number 39 pp. Thomson English physicist who helped revolutionize the knowledge of atomic structure by his discovery of the electron 1897.
Thomson proposed the plum pudding model of the atom which had negatively-charged electrons embedded within a positively-charged soup. Lived 1856 - 1940. He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1906 and was knighted two years later.
Thomson suggested that the model of an atom as a sphere of positively charged matter with negatively charged electrons surrounding them. This was the first sub-atomic particle to ever be discovered shocking all scientists in the world. Thomson theorized that electrons were surrounded by a positively charged material.
In March 1904 JJ Thomson proposed a model of the atom whereby the negatively charged corpuscles electrons were distributed in a uniform sea of positive charge and electrostatic forces determined their position. Thomsons model showed the atom as a positively charged ball of matter with negatively chaged electrons floating freely around inside of it. An Investigation of the Stability and Periods of Oscillation of a number of Corpuscles arranged at equal intervals around the Circumference of a Circle.
With this new info he created the Plum-Pudding model of the atom in which the electrons were inside of the atom itself. He stated that electrons were positioned by electrostatic forces. There were some inconsistency in his atomic theory and his atomic model.
First we are going to travel back a little over 2000 years ago to the times of Aristotle and Democritus. Thomson took science to new heights with his 1897 discovery of the electron - the first subatomic particle. Thomson began experimenting with a cathode ray tube which is shown in the diagram to the left.
Known as the Plum Pudding Model it played an important role in the research of atomic structure. Thomson had started to discover atomic theory that gives complete explanation of atomic structure. Thomson atomic model earliest theoretical description of the inner structure of atoms proposed about 1900 by William Thomson Lord Kelvin and strongly supported by Sir Joseph John Thomson who had discovered 1897 the electron a negatively charged part of every atomThough several alternative models were advanced in the 1900s by Kelvin and others Thomson held that atoms are uniform.
Thomsons greatest contribution to science to be his role as a teacher. His atomic theory helped explain atomic bonding and the structure of molecules. This model showed the atom having no structure.
Thomson contributed extensively to the field of chemistry by discovering the existence of electrons developing the mass spectrometer and determining the presence of isotopes. Thomson discovered the natural radioactivity of the element potassium in 1905 and he demonstrated that the hydrogen atom contained only a single electron in 1906. Joseph John Thomsons contributions to science helped revolutionize the understanding of atomic structure.
History of the atomic theory. Thomson was closely aligned with chemists of the time. Thomson also had a theory of what was known as the plum pudding model which posited that electrons orbited within a sea of positive charge.
Limitations of Atomic Theory by JJ Thomson. Since the atomic model constructed by JJ Thomson was one of the earliest atomic theory its understandable that his atomic theory still contains some flaws. Proposed a theory for the hydrogen atom based on quantum theory that energy is transferred only in certain well defined quantities.
Thomson 1904 On the Structure of the Atom. This model explained the description of an inner structure of the atom theoretically. Thomson An addition to Daltons atomic theory occurred in 1897 when English physicist JJ.
Symbolic interaction theory or symbolic interactionism is one of the most important perspectives in the field of sociology providing a key theoretical foundation for much of the research conducted by sociologists. While it might seem like a big name symbolic interactionism is how your experiences add subjective meanings to symbols and letters.
 Symbolic Interactionism Video Khan Academy
Symbolic Interactionism Video Khan Academy
Symbolic interactionism focuses on looking at the actions and interactions among the individuals rather than at the group level.

Symbolic interaction theory definition. The notion of this approach is traceable to the introductory psychology of James William with the main interactionists being John Dewey Herbert Mead. This meaning is symbolic. Subjective meanings are given primacy because it is believed that people behave based on what they believe and not just on what is objectively true.
Symbolic interactions are intentional and convey meaning Blumer leaves out unintentional unsymbolic ones such as reflexes. Blumers symbolic interactionism is a theory in sociology that focused in the 1930s on the study of interaction between people and brought in field studies as the data collection method of choice Blumer 1968. Ashley Crossman states on About that this theory is a major framework of sociological theory.
The basic premise of this theory lies in the fact that individuals use the process of communication to give meaning to the things around them also others around them. Communicationthe exchange of meaning through language and symbolsis believed to be the way in which people make sense of their social worlds. They notice that as we interact with the world we change the way we.
A person labeled as a deviant may accept that deviant label by coming to view himself or herself as a deviant ie internalizing the label and then engaging in further behavior that is both consistent with the label and the way in which the label was applied. Etymology of Symbolic Interactionism Herbert Blumer 19001986 is credited with coining the term. Symbolic interaction is a process.
For example the word dog is just a series of letters. Symbolic interactionism is used within the field of sociology the study of human society to explain social behavior in terms of how people interact based on their interpretation of symbols. To an interpretive sociologist reality is subjective and relies less on scientific data and more on learning through interaction with others on a micro level scale.
It is a framework that helps understand how society is preserved and c. The symbolic interactionism analysis society by the descriptive meanings that people have given to objects events and behaviors. But it doesnt just stop there.
Afterward the journal of Meads Mind self and society brought the age of inquiry. According to this theory people live both in the natural and the symbolic environment. In line with symbolic interactionism labeling theorists state that the reaction of the society the community or a social group will affect the rule-breaker in one critical way.
Symbolic interaction is one of the several theories in the social sciences. Symbolic interaction theory analyzes society by addressing the subjective meanings that people impose on objects events and behaviors. Symbolic Interactionism is the way we learn to interpret and give meaning to the world through our interactions with others-.
Definition of Symbolic Interactionism noun The theory that society is possible because of the shared meanings and social patterns created during social interactions. SYMBOLIC INTERACTION THEORY 2 Symbolic Interaction Theory According to Manford Kuhn the foundation of social interaction advanced during oral tradition. Symbolic interactionism is an approach used to analyze human interactions by focusing on the meanings that individuals assign to things in the world around them including words and objects.
The symbolic interaction theory also called symbolic interactionism is defined by Dictionary Reference as a theory that human interaction and communication are aided by words gestures and symbols with conventionalized meanings. In other words it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds and in return how these worlds shape individual behaviors. Symbolic interactionism tends to focus on the language and symbols that help us give meaning to the experiences in our life.
Symbolic interactionism is a micro-level theory that focuses on the relationships among individuals within a society. Through your interactions with the letters dog you see this as a furry four-legged canine. Unlike positivist theory the Symbolic-Interaction Theory focuses on how individuals understand their actions and their surroundings.
Those adjustments that youre making can be explained by symbolic interaction theory also called symbolic interactionism a theory about social behavior and interaction. It is a sociological theory also known as a symbolic interaction perspective. Symbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to peoples particular utilization of dialect to make images and normal implications for deduction and correspondence with others.
People pass through each stage sequentially with the thinking at the new stage replacing the thinking at the previous stage. Kohlbergs research yielded three levels of moral development.
 Lawrence Kohlberg S Stages Of Moral Development Wikipedia
Lawrence Kohlberg S Stages Of Moral Development Wikipedia
Kohlbergs theory of moral development is based on the idea that as children get older their reasoning in moral dilemmas develops and becomes more sophisticated.

Kohlberg's theory of moral development. A series of moral dilemmas were presented to these participants and they were also interviewed to determine the reasoning behind their judgments of each scenario. The theory holds that moral reasoning a necessary condition for ethical behavior has six developmental stages each more adequate at responding to moral dilemmas than its prede. Stages of Moral Development According to Kohlberg Summary At stage 1 children think of what is right as that which authority says is right.
Obedience and Punishment 2. Each level has two distinct stages. Kohlbergs theory of moral development also seems to have a troubling normative aspect that is it seems to suggest that certain kinds of moral reasoning are better than others.
Lawrence Kohlbergs theory on moral development can be applied to the classroom where rules standards and consequences are concerned. The three levels of moral reasoning include preconventional conventional and postconventional. Proposed that moral development is a continual process that occurs throughout the lifespan.
Level 1 or Pre-Conventional Morality typically seen in young children between the ages of 4 and 10 years old. According to his theory cognitive development leads to moral development. Lawrence Kohlbergs theory claims that our development of moral reasoning happens in six stages.
The Theory of Moral Development formulated by Lawrence Kohlberg states that our judgments toward the rightness or wrongness of an action may be explained by different levels and stages of moral development. Lawrence Kohlberg expanded on the earlier work of cognitive theorist Jean Piaget to explain the moral development of children which he believed follows a series of stages. Kohlberg has focused on moral development and has proposed a stage theory of moral thinking which goes well beyond Piagets initial formulations.
Doing the right thing is obeying authority and avoiding punishment. Biography Lawerence Kohlberg born in 1927 Grew up in Bronxville New York Died on January 17th 1987 at the age of 59 Kohlberg became a professor of education and social psychology at Harvard in 1968 His book on moral development is used by teachers around the world. He based his theory upon research and interviews with groups of young children.
Kohlbergs Stages of Moral Development. Preconventional conventional and postconventional. Kohlbergs theory proposes that there are three levels of moral development with each level split into two stages.
Used Piagets story-telling technique to tell people stories involving moral dilemmas. Gilligan instead suggested that Kohlbergs theory overemphasizes concepts such as justice and does not adequately address moral reasoning founded on the principles and ethics of caring and concern for others. Not everyone reached the highest stages in Kohlbergs theory.
Kohlberg suggested that people move through these stages in a fixed order and that moral understanding is linked to cognitive development. Understanding Kohlbergs theory of moral development can help to teachers to guide the moral development of their students in the classroom. They see that there are different sides to any issue.
This level consists of stage 1 and stage 2. Theory of Moral Development 8. We have explained the origins of the theory defined all six stages of moral reasoning according to Kohlberg and discussed some of the potential problems in both methodological and theoretical part of this theory.
Kohlberg proposed that there is a distinction between moral reasoning and moral behavior. Lawrence Kohlberg is well known for this theory of moral development. The theory tracks an individuals level of moral reasoning.
This of course presupposes certain moral assumptions and so from a philosophical perspective Kohlbergs argument is circular. Kohlberg began work on this topic while being a psychology graduate student at the University of Chicago in 1958 and expanded upon the theory throughout his life. This theory was founded on the results of Kohlburgs experiments with children using the Hienz Dilemma.
Kohlberg extended Piagets theory. That would be everything we wanted to tell you about Kohlbergs theory of moral development. Kohlberg who was born in 1927 grew up in Bronxville New York and attended the Andover Academy in Massachusetts a private high school for bright and usually wealthy students.
Kohlbergs theory on moral development 1. Lawrence Kohlbergs stages of moral development constitute an adaptation of a psychological theory originally conceived by the Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. At stage 2 children are no longer so impressed by any single authority.
Kohlbergs Theory on Moral Development Adolescent Psychology 2. Moral reasoning refers to the ability to make distinctions between right and wrong. Kohlbergs theory focuses on the thinking process that occurs when deciding whether a behaviour is right or wrong.
Kohlberg believed that women tended to remain at the third level of moral development because they place a stronger emphasis on things such as social relationships and the welfare of others. Kohlberg defined three levels of moral development. Lawrence Kohlbergs stages of moral development comprehensive theory developed by Kohlberg in 1958 based on Jean Piagets theory of moral judgment for children.
Each level consisted of two stages leading to six stages in total.
It was used to justify American military involvement in several countries beginning in the 1940s. Support for colonialist FRANCE and later dictatorial governments of South VIETNAM in Indochina against what it read as a communist insurgency compounded by a communist invasion.
 Domino Theory The Theory That A Political Event In One Country Will Cause Similar Events To Happen In Ne World History Teaching Cold War World History Lessons
Domino Theory The Theory That A Political Event In One Country Will Cause Similar Events To Happen In Ne World History Teaching Cold War World History Lessons
Definition of domino theory.

What is the domino theory. The theory that a political event in one country will cause similar events in neighbouring countries like a falling domino causing an entire row of upended dominoes to fall. Domino Theory a theory of accident causation and control developed by HW. The domino theory was a Cold War policy that suggested a communist government in one nation would quickly lead to communist takeovers in neighboring states each falling like a perfectly aligned.
Heinrich it defines an accident as one factor in a sequence that may lead to an injury. The domino theory was a theory prominent in the United States from the 1950s to the 1980s that posited that if one country in a region came under the influence of communism then the surrounding countries would follow in a domino effect. The domino theory is one of several major theories concerning accident causation.
A theory that if one nation becomes Communist-controlled the neighboring nations will also become Communist-controlled. The domino theory was used by successive United States administrations during the Cold War to justify the need for American intervention around the world. The United States had been rattled by the so-called loss of China to the communist side in 1949 as a result of Mao Zedong and the Peoples Liberation Armys triumph over Chiang Kai-sheks Nationalists in the Chinese Civil War.
When they are close enough together knocking one down at the start of the line can cause the entire line of dominoes to eventually fall over. The domino theory was the rationale for US. The Domino Theory was a metaphor for the spread of communism as articulated by US President Dwight D.
The Domino theory is based on the idea of what happens when a series of dominos are placed in a row. Domino theory theory adopted in US. If one country in a region came under the influence of communism then the surrounding countries would follow in a domino effect.
Developed by the safety engineer H. The theory that if one act or event is allowed to take place a series of similar acts or events will follow. The domino theory which governed much of US.
He explained that Laos a country of 2 million was a sovereign state whose people desired to be independent. Among these theories Domino theory is renowned one. This theory was developed by Late HW.
Foreign policy after World War II according to which the fall of a noncommunist state to communism would precipitate the fall of noncommunist governments in neighboring states. He was an Assistant. Heinrich that purports that all accidents whether in a residence or a workplace environment are the result of a chain of events.
Accident could be significant such as a broken bone or concussion. An accident could be minor such a laceration to the finger. Eisenhower in an April 7 1954 news conference.
Pure Chance theory Birds accident triangle Domino Theory Energy transfer theory accident proneness theory. The domino theory was a Cold War policy that suggested a communist government in one nation would quickly lead to communist takeovers in neighboring states each falling like a perfectly aligned row of dominos. Heinrich Herbert William Heinrich in 1931He was an American industrial safety pioneer from the 1930s.
This domino theory was used by the US administration to justify the need for American intervention in various parts of the world. Domino theory definition a theory that if one country is taken over by an expansionist especially Communist neighbor party or the like the nearby nations will be taken over one after another. Construction safety and the OSHA standards.
In a 1963 press conference President John Kennedy expanded the domino theory to LAOS. The final domino in Heinrichs theory is the actual injury to an individual. Heinrich in the 1950 edition of his book Industrial Accident Prevention.
The domino model of accident causation as depicted by H. Foreign policy beginning in the early 1950s held that a communist victory in one nation would quickly lead to a chain reaction of communist takeovers in neighboring states.