Nearly 60 of your body is water and this amount ranges from 45 to 75 depending on your physiological properties and daily habits. The right amount differs depending on factors such as body weight level of physical activity the climate and whether they are breastfeeding.
 How Does Water Affect The Human Body
How Does Water Affect The Human Body
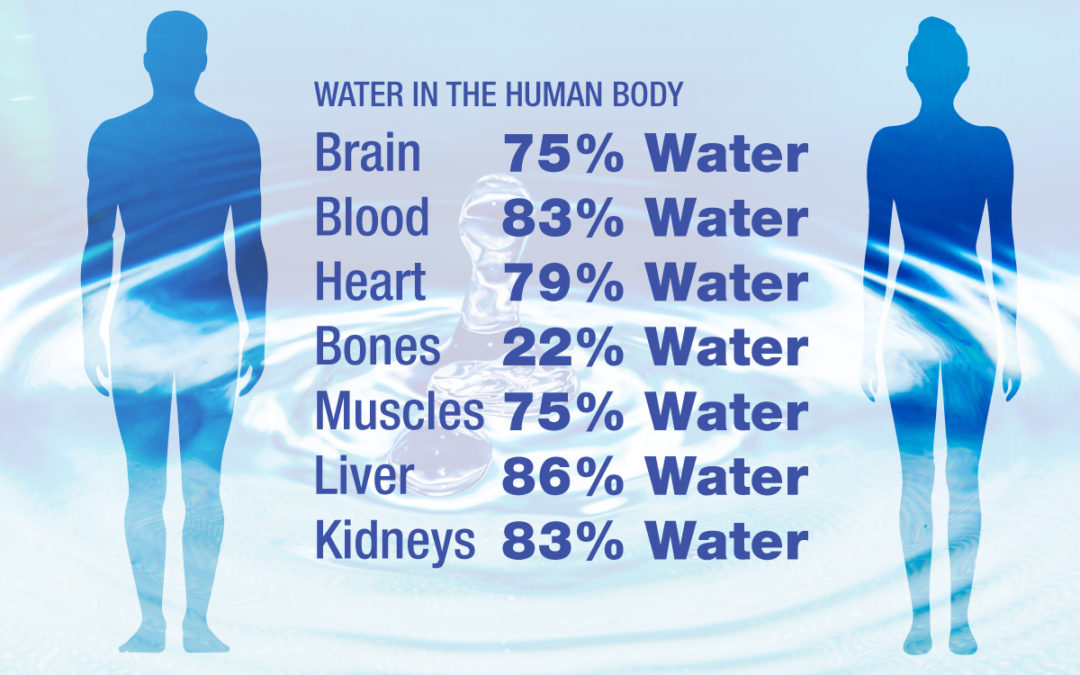
Organs like your heart lungs kidneys liver and brain all contain significant volumes of water ranging from 64-83.

How much of your body is water. After 50 your body is sapped even more with men at around 55 percent water and women at 47 percent. Even your bones which have comparatively lower water content are still about 31 water. Thats even more incredible when you consider that the body is around 60 per cent water so losing 11 body mass means shedding almost twice that in terms of water content.
In 2004 The National Academy of Medicine. The amount of water in the human body ranges from 50-75. While the average percentage of water in a.
This gives you an overview whether you are in a healthy range for percentage or not. During this dynamic cycle water is lost during urination and sweating and regained by your daily liquid and food consumption. The figure for water fraction by weight in this sample found to be 58 8 water for males and 48 6 for females.
Click on the Calculate button to generate the results. The skin contains 64 water muscles and kidneys are 79 and even the bones are watery. Water makes up an estimated 60 of your body weight.
The percentage of water in infants is much higher typically around 75-78 water dropping to 65 by one year of age. Up to 60 of the human adult body is water. How Water is Beneficial for Your Health.
Most of the human body is water with an average of roughly 60. The average adult human body is 50-65 water averaging around 57-60. Most mature adults lose about 25 to 3 litres of water per day.
Mitchell Journal of Biological Chemistry 158 the brain and heart are composed of 73 water and the lungs are about 83 water. However this varied substantially by age sex and adiposity amount of fat in body composition. Elderly people lose about two litres per day.
In male adults the water percentage is about 60 although lean tissues have more water compared to fat tissues. Though the actual average percentages of water in the human body vary by gender age and weight one thing is consistent. The amount of water in the body changes slightly with age sex and hydration levels.
Input the workout duration in total minutes per day. Infants consist of more water than adults. Men typically consist of more water than women.
By adulthood the differences are even more pronounced. It is a critical chemical component that your body depends on to survive. Water is your bodys principal chemical component and makes up about 50 to 70 of your body weight.
The human body ranges from 50 to 75 water. Water in our body parts. Your body depends on water to survive.
Normally trying to drink the right amount of water every day can fix this side note. The amount of water in the human body ranges from 45-75. Infants and young childrens bodies contain even more water newborns have about 75 water in their bodies at birth.
The average adult human body is 50-65 water averaging around 57-60. Starting at birth more than half of your body weight is composed of. Therefore they have bodies made of about 55 water.
To obtain the percentage of body water presume 1 liter 1 kilogram. Water loss may increase in hot weather and with prolonged exercise. Adult women have more fat making up their body than men.
An air traveller can lose approximately 15 litres of water during a three-hour flight. The correct amount of water for you is half your weight in ounces meaning a 150lb person should drink 75 ounces per day equal to 225 liters but most people dont drink that much. Next divide your Total Body Weight or TBW by your weight.
Although this water is not stable it is lost and gained many times throughout the day. In a large study of adults of all ages and both sexes the adult human body averaged 65 water. Body of a new born consists of 75 of water and an elderly individual can be a little more than 50 of.
The percentage of water in infants is much higher typically around 75-78 water dropping to 65 by one year of age. Body water content is higher in men than in women and falls in both with age. Overweight people contain a lower percentage of water than lean people.
Adult men are around 60 percent water while adult women average around 50 percent. Every cell tissue and organ in your body needs water to work properly. Input your full body weight in kilos or pounds.
The veins of the head and neck may be subdivided into three groups. Some capillaries are just one-third as wide as a human hair.
 Diagram Pulmonary Vein Body Diagram Full Version Hd Quality Body Diagram Givediagram Virtual Edge It
Diagram Pulmonary Vein Body Diagram Full Version Hd Quality Body Diagram Givediagram Virtual Edge It
Varicose veins are twisted enlarged veins.

Veins of the body. But if you removed all the blood vessels from an adults body and laid them out they would stretch nearly 100000 miles. It connects veins and arteries. They consist of two distinct sets of vessels the pulmonary and systemic.
They can be a sign of a deeper circulation problem Malvehy says. The deep veins accompany the major arteries and their branches and are usually paired. 3 The diploic veins the veins of the brain and the venous sinuses of the dura mater.
Veins are the large return vessels of the body and act as the blood return counterparts of arteries. Cervical plexus C1-C5 12 cranial nerves. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart for reoxygenation.
Internal jugular external jugular anterior jugular subclavian and brachiocephalic veins Nerves. Ophthalmic veins and emissary veins. A list of veins in the human body.
These are two similar yet different types of blood vessels forming the parts of the circulatory system. Veins are a critical part of normal circulation in the body so varicose veins can be more than just a cosmetic issue. The veins of the upper extremity and thorax.
The Veins of the Exterior of the Head and FaceThe veins of the exterior of the head and face Fig. They receive blood from the arteries via the arterioles and capillaries. THE VEINS convey the blood from the capillaries of the different parts of the body to the heart.
The Systemic Veins return the venous blood from the body generally to the right atrium of. Superficial veins are located close to the surface of the skin and are not located near a corresponding arteryDeep veins are located deep within muscle tissue and are typically located near a corresponding artery with the same name. The veins of the head and neck The veins of the exterior of the head and face.
Systemic veins return deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body to the heart. A vein can range in size from 1 millimeter to 1-15 centimeters in diameter. The veins of the brain.
The superior vena cava carries blood from the arms and head to the right atrium of the heart while the inferior vena cava carries blood from the legs and abdomen to the heart. The smallest veins in the body are called venules. 2 The veins of the neck.
The venules branch into larger veins which eventually carry the blood to the largest veins in the body the vena cava. Spider veins appear as thin red lines or as weblike networks of blood vessels on the surface of the skin. Capillaries are smaller and thinner than the arteries and veins of the body and are connecting blood vessels.
The deep veins are these posterior tibial veins and the peroneal veins and the superficial veins are the saphenous veins the long saphenous which runs all the way down the medial aspect and the short saphenous which comes off the popliteal vein here. The superficial veins are located within the subcutaneous tissue whilst the deep veins are found deep to the deep fascia. The Pulmonary Veins unlike other veins contain arterial blood which they return from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
Because the arteries arterioles and capillaries absorb most of the force of the hearts contractions veins and venules are subjected to very low blood pressures. FIG557 Veins of the head and neck. Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
In a metaphorical sense veins are the. When blood has been pumped by the heart to various parts of the body it must return back to the heart. Arteries and veins are the pipe-like vessels that carry blood in the body.
The veins of the neck. Arteries and veins are two of the bodys main type of blood vessels. The sinuses of the dura mater.
1 The veins of the exterior of the head and face. Veins on the other hand are denoted blue and its meant to carry oxygen-poor and carbon-dioxide-rich blood back to the heart. Veins are a type of blood vessel that return deoxygenated blood from your organs back to your heart.
The largest veins in the human body are the venae cavaeThese are two large veins which enter the right atrium of the heart from above and below. Its nearly impossible to count the actual number of veins arteries and capillaries in the human body because of their size. These are different from your arteries which deliver oxygenated blood from your heart to the.
The veins of the heart. They are located within a vascular sheath with the corresponding artery which helps compress and move blood within the veins. Veins serve a critical function within our bodies.
Olfactory CN I optic CN II oculomotor CN III trochlear CN IV trigeminal CN V abducens CN VI facial CN VII vestibulocochlear CN VIII glossopharyngeal CN IX vagus CN X accessory CN XI and hypoglossal nerves CN XII. In general arteries carry away the blood pumped by the heart during systole. Spider veins a mild form of varicose veins typically appear on the legs and feet.
These are thin and located close to the skin surface. The inferior vena cava is retroperitoneal and runs to the right and.
These have a diameter of 0008 mm meaning a line of 125 red blood cells is only 1. Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
/types-of-cells-in-the-body-373388-v3-5b76f0ad46e0fb0050ba820e.png) 11 Different Types Of Cells In The Human Body
11 Different Types Of Cells In The Human Body
The human body is composed of trillions of cells.
Cells in the human body. No one type of cell is more important than the other because without all of the different types of cells the human body would not be able to function. Osteoclasts osteoblasts and osteocytes. Human body has a whooping 37 trillion cells.
Written by subject experts aligns with standards. These types are skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle. These are of different types like the nerve cell muscle cell bone cells secretory blood cells and more Cells in a human body are of different types based on their structure and function.
Osteoblasts regulate bone mineralization and produce osteoid an organic substance of the bone matrix which mineralizes to form bone. The majority of the cells in our bodies are actually red blood cells. Nerves cells are the communication system of the body.
The central body contains the nucleus and other. You need a microscope to see most human cells. There are three primary types of bone cells in the body.
Pancreatic cells can live for as long as a year. Osteoclasts are large cells that decompose bone for resorption and assimilation while they heal. It is the most common type of epithelial tissue in people.
They provide structure for the body take in nutrients from food convert those nutrients into energy and carry out specialized functions. You can find these cells in different parts of the body including the pharynx esophagus oral cavity uterine cervix vagina and skin. Also called neurons they consist of two major parts the cell body and nerve processes.
Certain cells of the digestive tract live for only a few days while some immune system cells can live for up to six weeks. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. Red blood cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body.
They can live anywhere from a few days to a year. The human body is the structure of a human beingIt is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systemsThey ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body. The study of the human body involves anatomy physiology histology and.
Stratified squamous cells are flat and are arranged in multiple layers. It comprises a head neck trunk which includes the thorax and abdomen arms and hands legs and feet. In humans there are many different types of stem cells that come from different places in the body or are formed at different times in our lives.
There are 3 types of muscle cells known as myocytes in the human body. Cells within the human body have different life spans based on the type and function of the cell. Cells also contain the bodys hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
Each cell has a size and shape that is suited to its job. Different cells have different jobs to do. Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are known as striated due to the aligned arrangement of myosin and actin proteins within them.
Most plant and animal cells are only visible under a light microscope with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres. Red blood cells white blood cells and platelets. Your cells are the energy converters for your body.
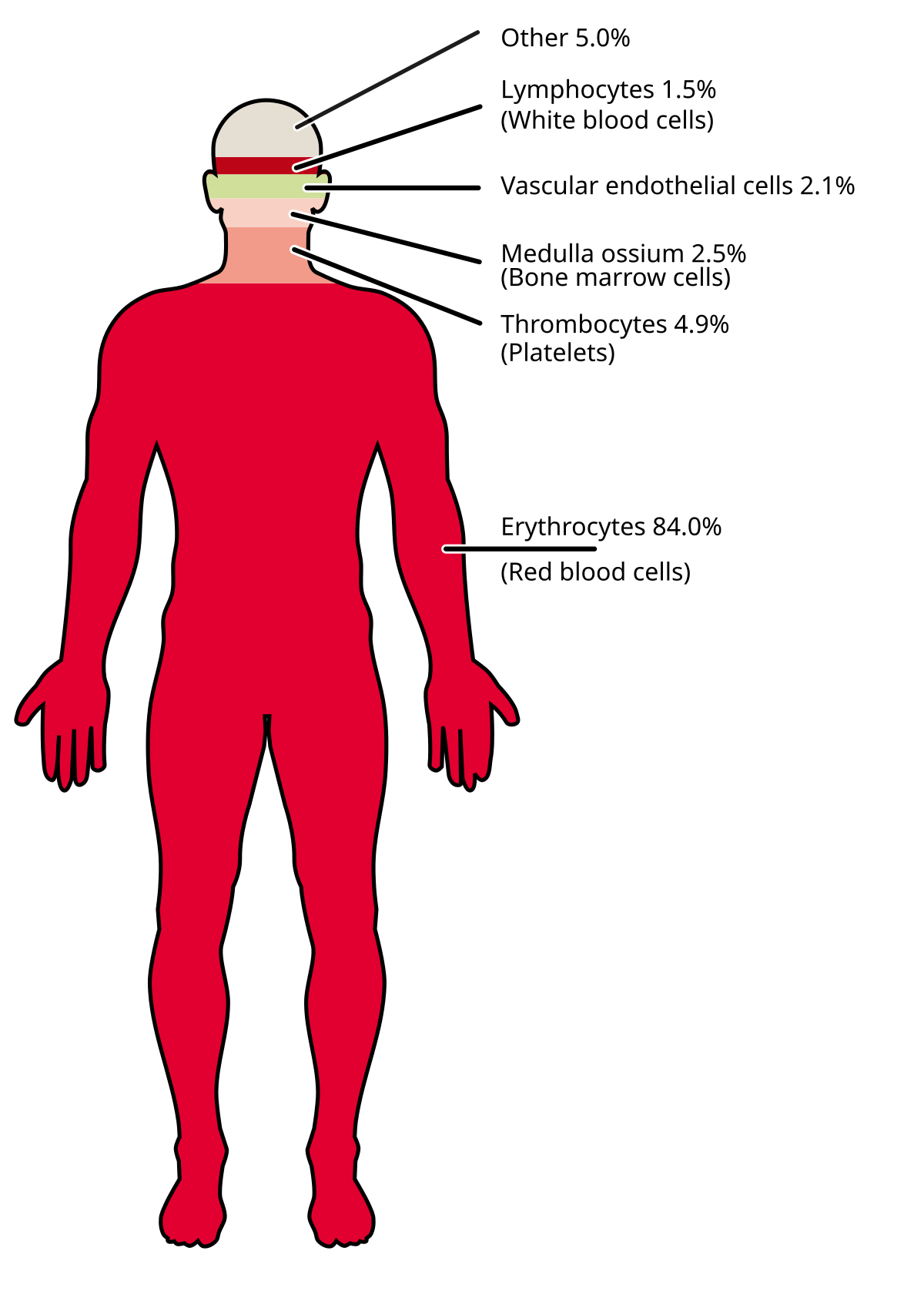
Red blood cells RBCs are by far the most abundant type of cell in the human body accounting for over 80. A team of scientists from Japan have found success in growing small intestinal cells akin to those found in the human body from human-induced pluripotent stem cells. There are three types of blood cells.
These include embryonic stem cells that exist only at the earliest stages of development and various types of tissue-specific or adult stem cells that appear during fetal development and remain in our bodies throughout life. Access 3 different reading levels perfect for Grades 3-8. Epithelial cells exist throughout the body and function as protective linings covering the insides and outsides of various organs.
From nerve cells and muscle cells to stem cells and sex cells there are myriad types of cells in the human body and their uses are just as variegated. Cells that do the same job combine together to form body tissue such as muscle skin or bone tissue. Electron microscopy gives a much higher resolution showing greatly detailed cell structure.
Gain instant access to this beautifully designed Unit on Cells where kids will learn all about Whats in a Cell What Cells Do DNA The Discovery and Study of Cells and more. These types are skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle. The scientists used a.
Although they make up over 80 percent of our body in number they constitute only around 4 percent of total body mass. They can be round box-shaped or flattened in structure and often have cilia tiny hairlike extensions on their surfaces to sweep away foreign materials.