It is an equation of state of an ideal gas that relates pressure volume quantity of gas and temperature. Ideal gas law A law that describes the relationships between measurable properties of an ideal gas.
It was first formulated by French physicist Emile Clapeyron in 1834.
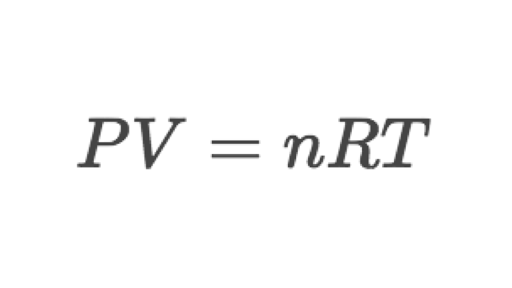
Ideal gas law definition. The ideal gas law is also known as the general gas equation. In thermodynamics we can say that the Ideal gas law is said to be a well-defined approximation of the behaviour that is of many gases under diverse conditions. An ideal gas is also known as a perfect gas.
In order to reach a simple form It takes the assumption that there is no interaction in between the molecules of the gas. While the law describes the behavior of a hypothetical gas it approximates the behavior of real gases in many situations. An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces.
Visit to learn more. An ideal gas can be visualized as a collection of perfectly hard spheres which collide but which otherwise do not interact with each other. Definition Formula Units Kinetic Theory of Gases In most usual conditions for instance at standard temperature and pressure most real gases behave qualitatively like an ideal gas.
The law states that P X V n X R X T where P is pressure V is volume n is the number of moles of molecules T is the absolute temperature and R is the gas constant 8314 joules per degree Kelvin or 1985 calories per degree Celsius. It is given as PVnRT where R is the ideal gas constant. Ideal Gas Law Formula.
The Ideal gas law is also known as general gas law. The equation of Ideal Gas is the combination which is of empirical laws like Charles law and the Boyles law then the Gay-Lussacs law and the law of Avogadros. It was first stated by Benoit Paul Emile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyles law Charless law Avogadros law and Gay-Lussacs law.
It is a good approximation to the behaviour of many gases under many conditions although it has several limitations. Also called universal gas law. This law states that.
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. The law combines Boyles law Avogadros law Gay-Lussacs law and Charles law. Ideal Gas law - Definition Equation Units Limitations Derivation.
One can visualize it as a collection of perfectly hard spheres which collide but which otherwise do not interact with each other. Many gases such as nitrogen oxygen hydrogen noble gases. Gas-scaletemperaturesTpandTbecomeidenticalifthegas obeys Boyleslawand as has just been saidtheir common value T becomeswith the proper choice of degrees identical with.
What is the Ideal Gas Law. On the other hand all real gases approach the ideal state at low pressures densities. The ideal gas law also called the general gas equation is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gasIt is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions although it has several limitations.
The term ideal gas refers to a hypothetical gas composed of molecules which follow a few rules. What is an elastic collision. As the name states the law is applicable under the ideal conditions not to real gases.
Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly eleastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces. The law was first stated by Emile Clapeyron in 1834. Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other.
It is derived from a combination of the gas laws of Boyle Charles and Avogadro. Validity of Ideal Gas Law Since ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces there is no such thing in nature as a truly ideal gas. The volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the number on moles of gas directly proportional to the temperature and inversely proportional to the pressure.
Ideal gases are defined as having molecules of negligible size with an average molar kinetic energy dependent only on temperature. It was first stated by Emile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyles law and Charless law. Perfect Gas law Avogadro Law The ideal gas law allows to represent the behavior of gases at low pressure.
A physical law describing the relationship of the measurable properties of an ideal gas where P pressure V volume n number of moles R the gas constant T temperature in Kelvin. Ideal Gas Law Definition. The ideal gases obey the ideal gas law perfectly.
The law correlates the pressure volume temperature and amount of gas. The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container. At a low temperature most gases behave enough like ideal gases that the ideal gas law can be applied to them.
The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law a simplified equation of state and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanicsThe requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if for example the interaction is perfectly. An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas equation is defined as the relationship between Boyles law Charles law Avogadros law.
A homogeneous mixture is a type of mixture with a uniform composition. The solvent is the substance doing the dissolving.
 Neutral Solution Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Neutral Solution Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
In an unsaturated solution the rate of dissolution is much greater than the rate of crystallization.
Scientific definition of solution. A solution consists of a solute and a solvent. 00002 2 x 10-4 where -4 is the negative exponent. Sə-loo shən Chemistry A mixture in which particles of one or more substances the solute are distributed uniformly throughout another substance the solvent so that the mixture is homogeneous at the molecular or ionic level.
A solution has certain characteristics. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A solution is made up of particles or solutes and a solvent.
Any state of matter solid liquid or gas can act both as a solute or as a solvent during the formation of a solution. Solutions must have a solute and a solvent. Generally there is a significant decrease in fiber diameters with an increase of solution conductivity whereas low solution conductivity results in insufficient jet.
When a solute often a solid is added to a solvent often a liquid two processes occur simultaneously. The unit of pressure at sea level is one atmosphere. A solution is a specific type of mixture where one substance is dissolved into another.
The solute is the substance being dissolved. Water is the most common solvent. What is Suspension in Science.
When the scientific notation of any small numbers is expressed then we use negative exponents for base 10. The scientific method is an empirical method of acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. Solution in chemistry a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in relative amounts that can be varied continuously up to what is called the limit of solubility.
Atmospheric pressure the pressure exerted by the atmosphere usually considered as the downward pressure of air onto a unit of area of the earths surface. Go here to learn more about mixtures. Liquid solutions such as sugar in water are the most common kind but there are also solutions that are gases or solids.
This means that the substances cannot. The term solution is used to describe homogeneous mixtures with small particles. Pressure decreases with.
A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture that is made up of two or more substances. The term solution is commonly applied to the liquid state of matter but solutions of gases and solids are possible. Arterial pressure arterial blood pressure blood pressure def.
The solvent part of the solution is usually a liquid but can be a. Convert 000000046 into scientific notation. The American Heritage Science Dictionary Copyright 2011.
In chemistry a solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. The mixing process of a solution happens at a scale where the effects of chemical polarity are involved resulting in interactions that are specific to solvation. Dissolution is the dissolving of the solute into the solvent.
Solution - definition of solution by The Free Dictionary Solution conductivity is mainly determined by the polymer type solvent used and the availability of ion sable salts. The solution usually has the state of the solvent when the solvent is the larger fraction of the mixture as is commonly the case. There is usually more solvent than solute in any given solution.
Pressure P preshur force per unit area. Heat of solution definition is - the heat evolved or absorbed when a substance dissolves. Solid solution mixture of two crystalline solids that coexist as a new crystalline solid or crystal lattice.
A solution is the same or uniform throughout which makes it a homogeneous mixture. The amount involved when one mole or sometimes one gram dissolves in a large excess of solvent. How to use solution in a sentence.
Move the decimal point to the right of 000000046 up to 7 places. Solution definition is - an action or process of solving a problem. In such a mixture a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance known as a solvent.
Crystallization is the opposite process where the reaction deposits solute. A substance that can dissolve another substance or in which another substance is dissolved forming a solution. - Definition Types Examples.
A solution may exist in any phase. It involves careful observation applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed given that cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the observationIt involves formulating hypotheses via induction based on such observations. The solute is the substance that is dissolved in the solvent.
We are giving a detailed and clear sheet on all Physics Notes that are very useful to understand the Basic Physics Concepts. Triple point of water.
 Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
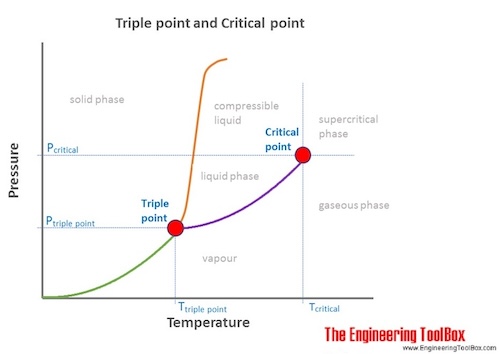
Point A is triple point where all three physical states of matter co exist.

Triple point definition chemistry. Describe what one would see at pressures and temperatures above 5 atm and 1000C. The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid solid and gaseous states. It is a specific case of thermodynamic phase equilibrium.
The values of pressure and temperature at which water coexists in equilibrium in all three states of matter ie. A substance is said to be at its critical point when the absolute temperature associated with it is equal to its critical temperature and the pressure applied to it is equal to its critical pressure. It describes a specific thermodynamic state of matte.
The term triple point was coined by James Thomson in 1873. The term triple point was coined in 1873 by James Thomson brother of Lord Kelvin. Critical Point Definition.
The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid solid and gaseous states. For example the triple point of Acetylene occurs at -807 Celsius. Ice water and vapour is called triple point of water.
Sometimes the triple point may involve more than one solid phase when there are polymorphs of the substance exist. For example the triple point temperature of mercury is at 388344 C at a pressure of 02 MPa. The number given for the temperature of the triple point of water is an exact definition rather than a measured quantity.
The triple point of pure water is at 001C 27316K 3201F and 458 mm 6112Pa of mercury and is used to calibrate thermometers. The triple point of water is the point where one is interested in all three phases of water at a certain pressure and temperature. Triple Point The three-phase equilibrium lines meet at one point.
The value of the triple point of water was fixed by definition rather than measured but that changed with the 2019 redefinition of SI base units. The triple point of water is used to define the kelvin the SI base unit of thermodynamic temperature. Watch how water behaves at the triple point where it co-exists in solid liquid and vapour form.
1-solid 2-liquid 3-gas 4-supercritical fluid point O-triple point C-critical point -785 C The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -785 C 2. Meaning pronunciation translations and examples. In physics and chemistry the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which three phases gas liquid and solid of that substance may coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Triple point of water synonyms Triple point of water pronunciation Triple point of water translation English dictionary definition of Triple point of water. Chemistry chem the temperature and pressure at which the. Rank the states with respect to increasing density and increasing energy.
This triple point is the point where the temperature and pressure conditions are right for all three states solid liquid and gas. The critical point is the end point of a phase equilibrium curve defined by a critical pressure T p and critical temperature P cAt this point there is no phase boundary. The triple points of several substances are used to define points in the ITS-90 international temperature scale ranging from the triple point of hydrogen 138033 K to the triple point of water 27316 K 001 C or 32018 F.
The temperature and pressure at which a substance co-exist in thermodynamic equilibrium with its three physical states solid liquid gas is know as triple point. The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which it can exist in all three states. This experiment demonstrates the triple point of a substance.
The triple point of water occurs at an external pressure of 18 in and a temperature of 3202F In strict terms this process is desiccation not lyophilization because water removal is done at temperatures above the triple point of water Is there a formula to calculate the triple point of a substance. The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid liquid and vapour phases of a particular substance coexist in equilibrium. In a phase diagram The critical point or critical state is the point at which two phases of a substance initially become indistinguishable from one another.
In chemistry and physics the triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid liquid and vapor phases of a particular substance coexist in equilibrium. The temperature and pressure at which the three phases of a substance are in equilibrium. What Is Triple Point.
Triple Point of Water Definition. The triple point is a Thermodynamic Phenomenon It is a point where an element exists in Solid Liquid and Gaseous form and in Thermodynamic Equilibrium.
In other words a chemical change is a chemical reaction involving the rearrangement of atoms. A chemical change is a change of materials into another new materials with different properties and one or more than one new substances are formed.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TC_608334-chemical-change-examples-5aabebea31283400371a753e.png) Chemical Change Examples In Chemistry
Chemical Change Examples In Chemistry
When a substance undergoes a physical change its composition remains the same despite its molecules being rearranged.
Chemical change definition chemistry. Instead the atoms rearrange themselves to form new chemicals. A chemical change is a type of change where the chemical properties of matter change. A chemical reaction is a process that occurs when one or more substances are changed into one or more new substances.
This happens because atoms are rearranging themselves. When a chemical reaction occurs atoms are neither created nor destroyed. A precipitate appears in a liquid or a gas an odour is detected bubbles appear increase or decrease in temperaturelight is emitted or a flame appears there is a change in colour.
During a chemical change bonds between the molecules break and the composition of the substance change. The formation of rust on iron is a chemical change. This is known as a chemical change.
Physical change is a temporary change. The changes in Chemical change are irreversible and permanent. Chemical change - chemistry any process determined by the atomic and molecular composition and structure of the substances involved chemical action chemical process chemical science chemistry - the science of matter.
Chemical changes take place at the molecular level. The branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions. These processes are called chemical reactions and in general are not reversible except by further chemical reactions.
It results when a substance combines with another to form a new substance synthesis or either decomposes to form more substances. In contrast physical changes do not form new products and are reversible. Examples of chemical changes include combustion burning cooking an egg rusting of an iron pan and mixing hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to make salt and water.
When a substance undergoes a chemical change its molecular composition is changed entirely. The change in which the molecular composition is completely altered and a new product is formed is called a chemical change. Or the investigation of new chemical products.
Examples of physical changes are boiling melting freezing and shredding. Zinc Zn is a silver-gray element that can be ground into a powder. Chemical changes create a new product.
It is commonly called a chemical reaction. Types of chemical change Changes are mostly of two types. Examples of chemical changes are burning cooking rusting and rotting.
A chemical reaction is where a substance changes into another substance. A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction results in a new product.
Some reactions produce heat and are called exothermic reactions and others may require heat to enable the reaction to occur which are called endothermic reactions. Chemical Change Definition A chemical change can be defined as a chemical reaction in which one or more substances undergo changes to form new substances or a new structure. Another way to think of it is that a chemical change accompanies a chemical reaction.
According to this property substances show variation in their reactivity. Chemical Change - the result of a reaction which creates one of more substances with different chemical properties Chemical Property - the chemical traits of matter or the potential of matter to react in a particular way. Thus chemical changes involve the formation of new substances.
Chemical changes involve chemical reactions and the creation of new products. A chemical change produces a new substance. Chemical changes occur when a substance combines with another to form a new substance called chemical synthesis or alternatively chemical decomposition into two or more different substances.
Often physical changes can be undone if energy is input. It reveals that chemical change cannot be reversed by changing or altering the experimental changes. A chemical change occurs when a new substance is formed through a chemical reaction like when fruit ripens or rots.
One chemical reaction can involve multiple substances changing form. The oxidation reaction is a chemical change example that causes a. When something undergoes a chemical reaction and a new substance is formed as a result we call this chemical change.
Typically a chemical change is irreversible. Different substances have different chemical property. A chemical change also known as a chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances are altered into one or more new and different substances.
In some instances simply applying heat can cause a chemical change. A chemical change results from a chemical reaction while a physical change is when matter changes forms but not chemical identity. Chemical change definition a usually irreversible chemical reaction involving the rearrangement of the atoms of one or more substances and a change in their chemical properties or composition resulting in the formation of at least one new substance.
It is the mass of a mole of a substance. What is Atomic Mass.
 How To Calculate Atomic Mass Atoms And Molecules For Kids Teaching Chemistry Atom
How To Calculate Atomic Mass Atoms And Molecules For Kids Teaching Chemistry Atom
The atomic mass of an element is frequently used by chemists to determine the amount of substance required in a chemical reaction.
Atomic mass definition chemistry. The mass number reports the mass of the atoms nucleus in atomic mass units amu. It relates the mass of an element to the number of atoms. The relative atomic mass of an element is a weighted mean mass of the isotopes of an element compared with that of the 12C isotope which has a mass of exactly 12.
The daltonor unified atomic mass unitsymbols. It is defined as 112 of the mass of an unboundneutral atom of carbon-12in its nuclear and electronic ground stateand at rest. Definition of Atomic Mass Atoms are the basic units of matter.
The atomic mass is the sum of the mass of protons neutrons and electrons. Atomic Mass Unit AMU The periodic table of elements contains every atom known to mankind. Daor u is a unitof masswidely used in physics and chemistry.
The mass of an atom or a molecule is referred to as the atomic mass. Each unique atom has a unique atomic number and atomic mass. One atomic mass unit is equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon 12 isotope.
The number of protons in an atom of an element is called the atomic number Z. The atomic mass is used to find the average mass of elements and molecules and to solve stoichiometry problems. Medical Definition of atomic mass unit.
The mass number A of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom of that element. The symbol used for it is M. It is denoted by ma.
Atomic mass - chemistry the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units atomic weight relative atomic mass mass - the property of a body that causes it to have weight in a gravitational field. The sum of the mass number and the atomic number for an atom A-Z corresponds to the total number of subatomic particles present in the atom. Updated June 30 2019 In chemistry an atomic mass unit or AMU is a physical constant equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an unbound atom of carbon -12.
Atomic mass definition the mass of an isotope of an element measured in units formerly based on the mass of one hydrogen atom taken as a unit or on 116 00625 the mass of one oxygen atom but after 1961 based on 112 00833 the mass of the carbon-12 atom. Relative atomic masses do not. Mass is a basic physical property of matter.
It has a unit of the unified mass unit u or the atomic mass unit amu. Atomic mass indicates the size of an atom. G mol 1 is the standard unit for the molar mass.
The atomic mass constant denoted muis defined identically giving mu m12C12 1 Da. The atomic number is the number of protons. It is a unit of mass used to express atomic masses and molecular masses.
Atomic mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry. They are the smallest components of a chemical element which is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler material. Atomic Mass or Weight Definition Atomic mass which is also known as atomic weight is the average mass of atoms of an element calculated using the relative abundance of isotopes in a naturally occurring element.
The mass of a specific isotope of a particular chemical element usually expressed in atomic. Atomic mass of an element is the number of times an atom of that element is heavier than an atom of carbon taken as 12. The number of protons in an atom of an element is its atomic number.
A unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms molecules or nuclear particles equal to ¹₁₂ the mass of a single atom of the most abundant carbon isotope 12C called also dalton.