It is an equation of state of an ideal gas that relates pressure volume quantity of gas and temperature. Ideal gas law A law that describes the relationships between measurable properties of an ideal gas.
It was first formulated by French physicist Emile Clapeyron in 1834.
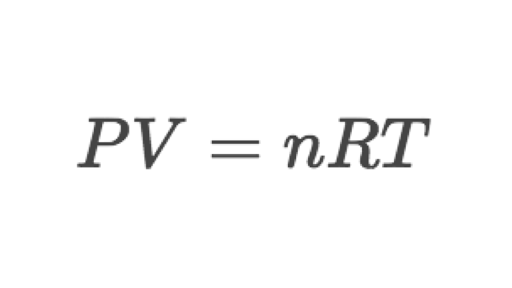
Ideal gas law definition. The ideal gas law is also known as the general gas equation. In thermodynamics we can say that the Ideal gas law is said to be a well-defined approximation of the behaviour that is of many gases under diverse conditions. An ideal gas is also known as a perfect gas.
In order to reach a simple form It takes the assumption that there is no interaction in between the molecules of the gas. While the law describes the behavior of a hypothetical gas it approximates the behavior of real gases in many situations. An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces.
Visit to learn more. An ideal gas can be visualized as a collection of perfectly hard spheres which collide but which otherwise do not interact with each other. Definition Formula Units Kinetic Theory of Gases In most usual conditions for instance at standard temperature and pressure most real gases behave qualitatively like an ideal gas.
The law states that P X V n X R X T where P is pressure V is volume n is the number of moles of molecules T is the absolute temperature and R is the gas constant 8314 joules per degree Kelvin or 1985 calories per degree Celsius. It is given as PVnRT where R is the ideal gas constant. Ideal Gas Law Formula.
The Ideal gas law is also known as general gas law. The equation of Ideal Gas is the combination which is of empirical laws like Charles law and the Boyles law then the Gay-Lussacs law and the law of Avogadros. It was first stated by Benoit Paul Emile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyles law Charless law Avogadros law and Gay-Lussacs law.
It is a good approximation to the behaviour of many gases under many conditions although it has several limitations. Also called universal gas law. This law states that.
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. The law combines Boyles law Avogadros law Gay-Lussacs law and Charles law. Ideal Gas law - Definition Equation Units Limitations Derivation.
One can visualize it as a collection of perfectly hard spheres which collide but which otherwise do not interact with each other. Many gases such as nitrogen oxygen hydrogen noble gases. Gas-scaletemperaturesTpandTbecomeidenticalifthegas obeys Boyleslawand as has just been saidtheir common value T becomeswith the proper choice of degrees identical with.
What is the Ideal Gas Law. On the other hand all real gases approach the ideal state at low pressures densities. The ideal gas law also called the general gas equation is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gasIt is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions although it has several limitations.
The term ideal gas refers to a hypothetical gas composed of molecules which follow a few rules. What is an elastic collision. As the name states the law is applicable under the ideal conditions not to real gases.
Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly eleastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces. The law was first stated by Emile Clapeyron in 1834. Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other.
It is derived from a combination of the gas laws of Boyle Charles and Avogadro. Validity of Ideal Gas Law Since ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces there is no such thing in nature as a truly ideal gas. The volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the number on moles of gas directly proportional to the temperature and inversely proportional to the pressure.
Ideal gases are defined as having molecules of negligible size with an average molar kinetic energy dependent only on temperature. It was first stated by Emile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyles law and Charless law. Perfect Gas law Avogadro Law The ideal gas law allows to represent the behavior of gases at low pressure.
A physical law describing the relationship of the measurable properties of an ideal gas where P pressure V volume n number of moles R the gas constant T temperature in Kelvin. Ideal Gas Law Definition. The ideal gases obey the ideal gas law perfectly.
The law correlates the pressure volume temperature and amount of gas. The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container. At a low temperature most gases behave enough like ideal gases that the ideal gas law can be applied to them.
The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law a simplified equation of state and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanicsThe requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if for example the interaction is perfectly. An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas equation is defined as the relationship between Boyles law Charles law Avogadros law.