The pH of an aqueous of the corresponding salt B A will be. Weak electrolytes do not.
 Acids And Bases Ph And Titrations Ppt Video Online Download
Acids And Bases Ph And Titrations Ppt Video Online Download
BaOH2 barium hydroxide.
H2so4 strong or weak. H2SO4 sulfuric acid. Strong electrolyte soluble and strong acid Chloric acid. In your first list H2SO4 is usually defined as strong but the ionization is two part.
When the strong acid has been completely. Identify each acid or base as strong or weak. Instructions For Electrolytic Behavior Table Light.
HSO4- already has a negative charge so its much harder to pull of an H. Account for the difference in strength of these two related species. The acids corrosiveness towards other.
MgOH 2 C 5 H 5 N. In this curve there are two break points. Indicate If The Substance Is A Strong Electrolyte Weak Electrolyte Or Non-electrolyte Substances Present In Solution.
Strong dehydrating acids H2SO4 H3PO4 favor elimination dehydration in alcohols. Because they are strong acids they readily protonate the alcohol thereby converting a poor leaving group OH- into a good leaving group HOH however the anions produced after protonation of the alcohol HSO4- or H2PO4- are very poor nucleophiles and can. H2SO4 H HSO4-.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound CaBr2. Hydrofluoric acid while a weak acid would pass through your hand and attack your bones. Sulfuric acid American IUPAC spelling or sulphuric acid traditional British spelling also known as oil of vitriol is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur oxygen and hydrogen with molecular formula H 2 SO 4It is a colourless and viscous liquid that is soluble in water and is synthesized in reactions that are highly exothermic.
HSO4- H SO4 but even without extra water it goes 95. Indicate If The Bulb Brightness Is Bright Dim Or No Light Observed Electrolyte. Therefore we refer to H2SO4 as a strong acid BUT only for the first proton that is released.
The HSO4- ion is a weak acid and only partially dissociates. For H2SO4 the proton leaves a neutral molecule. For that reason a 1 M solution of H2SO4 will NOT produce a 2M hydrogen ion concentration but instead it will produce just a little over 1 M hydrogen ions.
Conductometric titration of a weak acid acetic acid vs. - Hydrochloric Acid HCl - Hydrobromic Acid HBr - Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 - Perchloric Acid HClO4 - Nitric Acid HNO3 - Hydroiodic Acid HI - Periodic Acid HIO4 - Chloric Acid HClO4 Strong Bases. The second ionization may not go 100 unless extra water is used.
Because MgOH 2 is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong base. HNO2 nitrous acid. A Strong Base or a Weak Base.
The p K b of a weak base B O H is 4. Strong Weak And Nonelectrolytes. ACID BASE HCI CI- H2SO4 HSO4- - Negligible Strong- HNO3 NO3- H30 H20 HSO4 so2- H2SO3 HSO3- H3PO4 H2PO4 HF F- CH3COOH CH3CO0- H2CO3 HCO- Weak H2S HS- Weak- HSO3- SO32- H2PO4- HPO42- HCN CN- NH4 NH3 HCO3- Co22- HPO42- PO43- H20 On- HS- S2- Strong Negligible - On- 02- ACID STRENGTH BA SE STRENGTH.
H2SO4 is a strong acid but HSO4- is a weak acid. CH3COOH acetic acid. Strong electrolyte strong acid H2SO4.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound AlCl3. Tell What Substance Is Dissolved. HI hydroiodic acid.
Answer to H2SO4 is a strong acid but is a weak acid. Mixture of a Strong Acid and a Weak Acid vs. HF hydrofluoric acid.
Strong electrolyte ionic compound Perchloric acid. Account for the difference in strength of these two related species. Because HCl is listed in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases it is a strong acid.
HCN hydrocyanic acid. - Sodium Hydroxide NaOH. While acids tend to be corrosive the strongest superacids carboranes are actually not corrosive and could be held in your hand.
HCOOH formic acid. The first break point corresponds to the neutralization of strong acid. HBr hydrobromic acid.
The nitrogen in C 5 H 5 N would act as a proton acceptor and therefore can be considered a base but because it does not. The dissociation constant of two acids H A 1. Strong electrolyte strong acid Potassium hydroxide.
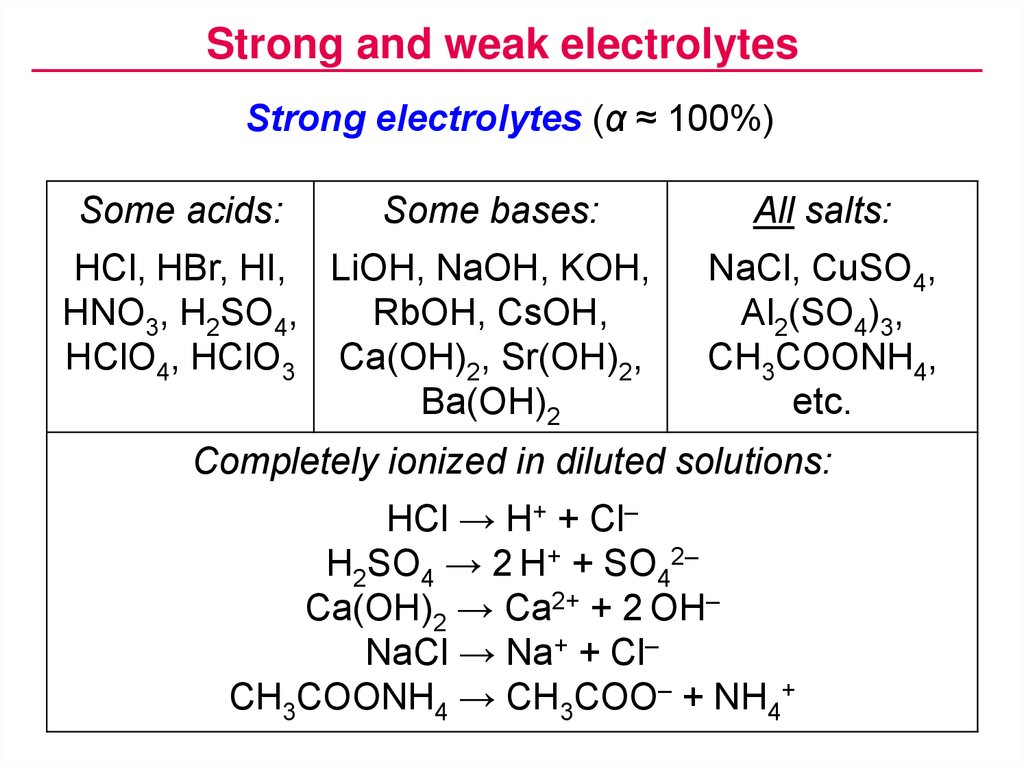
A strong acid or base is one that is completely ionized in a solution. Strong electrolytes ionize completely upon solvation. H2SO4 is a strong acid.
1 H2SO4 -- H HSO4-The remaining bisulfate ion HSO4- is a weak acid and only partially dissociates. A weak base NH 4OH 5. Choose strong acids from the following CH3COOH H2SO4HNO3H2CO3 - 5429451.
The reason is that sulfuric acid is highly corrosive while acetic acid is not as active. Strong electrolyte soluble and strong acid HNO3. Follow up.
It is a strong acid only for the first hydrogen ion that is produced.
The pH can be less than 7 not neutral for a weak acid and is typically lower than the value for a strong acid. List of Strong Acids.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png) List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids
List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids
A strong acid is one that dissolves in water.

List of strong and weak acids. The concentration of hydronium ions H 3 O in a dilute solution of a strong acid is equal to the concentration of the acid. Youll not only have to recognize the weak acids and bases but MEMORIZE the standard list of strong acids and bases listed on the cheat sheet below. There are only a few 7 strong acids so many people choose to memorize them.
If an acid is not listed here it is a weak acid. SrOH 2 - strontium hydroxide. In the equilibrium state the total concentration splits into its undissociated and.
The Acid Constants for Some Acids at 25C can be found here. C5H5N pyridine Remember any base that dissolves in water is an alkali and must have a pH above 7. Acids which do not get completely ionized in aqueous solution are called weak acids eg.
Here are their names and formulas. H 2 SO 4 sulfuric acid note. HClO 3 HBrO 3 HIO 3 H 2 SeO 4 Assume all other acids are weak unless told otherwise.
The strong acids are hydrochloric acid nitric acid sulfuric acid hydrobromic acid hydroiodic acid perchloric acid and chloric acid. Being part of the list of strong acids doesnt give any indication of how dangerous or damaging an acid is though. Strong acids completely dissociate in water into their ions and produce one of more protons or hydrogen cations per molecules.
The term strong in the name refers to the acids ability to release hydrogen H molecules which allows it to become ionized when placed into a solution of water. If it does not dissociate 100 it is a weak acid. HSO 4 is a weak acid HBr hydrobromic acid.
Strong and weak acids Strong acids dissociate fully in water to produce the maximum number of H ions. A strong base is a base that is 100 ionized in solution. Strong and Weak Acids and Bases 1.
HCl hydrochloric acid. Acids which get completely ionized in aqueous solution are called strong acids eghydrochloric acid nitric acid and sulphuric acid. What makes them strong is the fact that they completely dissociate into their ions H and an anion when they are mixed with water.
It may be 1 ionized or 99 ionized but it is still classified as a weak acid. Strong acids are not named as such because they are more powerful than other acids. There are seven strong acid.
When acids dissolve and ionize in water they form a dynamic equilibrium between reactants and products. HF HNO 2 HClO 2 H 2 SO 3 SO 2 H 2 O HC 2 H 3 O 2 HOAc 2. Strong and Weak Acids.
Chloric acid hydrobromic acid hydrochloric acid hydroiodic acid nitric acid perchloric acid and sulfuric acid. The issue is similar with bases. Any acid that dissociates 100 into ions is called a strong acid.
HCl HBr HI HNO 3 HClO 4 H 2 SO 4 The following are some less common acids that are also strong. All the other acids are weak. There are only 7 common strong acids.
There are only a few strong acids but many weak acids. This means if you had one mole of hydrochloric acid HCl molecules they would all split to. As you will see below the strength of an acid is related to the proportion of it which has reacted with water to produce ions.
Acetic acid citric acid and formic acid. RbOH - rubidium hydroxide. A classification based on acidity constants or pK a values seems natural.
HI hydroiodic acid. As it turns out there are very few strong acids which are given in Table 122 Strong Acids and Bases. This cheat sheet below is meant to accompany the MCAT AcidBase Tutorial Series math focus as well as the Orgo AcidBase Tutorial series trendsconcept focus.
The acid dissociation constant K a is a lower value for strong acids. Amount of H Ions Released. Hydrochloric acid citric acid acetic acid nitric acid formic acid sulphuric acid.
Lets denote the total amount of the acid by C T HA T which is de facto the acids initial concentration before it dissolves. This page explains the terms strong and weak as applied to acids. There are 7 strong acids.
Typical weak acids such as HF and CH 3 COOH have acid constants with a value of 10 4 or 10 5 mol dm 3. The strong acids and bases are simply those that completely dissociate in water. HNO 3 nitric acid.
Strong acids dissociate completely in water while weak acids do not dissociate completely. Strong acids completely dissociate into their ions in water while weak acids only partially dissociate. Strong acid - an acid that ionizes almost 100 in water producing hydrogen ions.
Every other acid is a weak acidBecause there are only seven strong acids it is easy to commit the list to memory. As it turns out there are very few strong acids which are given in Table PageIndex1. BaOH 2 - barium hydroxide.
Strong acids release all the H ions it can release to the solution. The pH of a weak acid solution is about 3-5. Notice that exceptions occur.
If an acid is not listed here it is a weak acid. The following common acids are strong. CsOH - cesium hydroxide.
For instance for a 1 mM solution the pH of hydrochloric acid is 301 while the pH of hydrofluoric acid is very low with a value of 327 for a 1 mM solution. It may be 1 ionized or 99 ionized but it is still classified as a weak acid. Mineral or inorganic acids tend to be strong acids.
Strong acid The acid that ionises completely in aqueous solution thus producing a high concentration of ions is called a strong acid eg HCI etc. As a part of this it defines and explains what is meant by pH K a and pK a. It is important that you dont confuse the words strong and weak with the terms concentrated and dilute.
Weak acids do not have this ability. Acids like the ammonium ion NH 4 and hydrogen cyanide HCN for which Ka is less than 10 9 mol dm 3 are very weakly acidic. N the following list of acids separate strong acids from weak acids.
In chemistry there are seven strong acids. The acid dissociation constant K a is a higher value for strong acids. CaOH 2 - calcium hydroxide.