As such our task in predicting the final pH of the solution is to. This is called a neutralization reaction and looks like this.
/pipette-beaker-56a12dcd5f9b58b7d0bcd148.jpg) How To Mix Acid And Water Safely
How To Mix Acid And Water Safely
The concept of an acid-base reaction was first proposed in 1754 by Guillaume-Francois Rouelle who introduced the word base into chemistry to mean a substance which reacts with an acid to give it solid form as a salt.
Mixing acid and base. Soap is formed once a robust base is additional to a carboxylic acid a building block of fats found in our bodies and food breaking it all the way down to kind a tough or soft soap depending on the base. Chlorine gas poisoning symptoms include breathing difficulties nose and throat irritation nausea and headaches. Depending on the bases and acids used it can be a dangerous experiment.
Also NaOH KOH are strong bases. In this lesson first we discuss about how to calculate pH of acidic solution of strong acids such as HCl H 2 SO 4. Mixing acids and bases When bound acids and bases ar mixed they will react to supply water and a salt.
Vresultant solution L Vresultant solution mL 1000 mLL Calculate the concentration of the reactant in excess. When u mix an acid with a base the reaction is a neutralization reaction. As you can see from the chemical formula the mixing of these two acids and bases produces chlorine gas.
Mixing a base with an acid results in a chemical reaction called neutralization. Thus a 1 M solution of H 2 SO 4 will be 2 N. Strong acid and strong bases titration curve.
Bases are chemical compounds that in solution are soapy to the touch and turn red vegetable dyes blue. Imagine mixing a weak acid and a weak base in equal amounts and concentrations. When mixing sulfuric acid or another strong acid start with a volume of water large enough to absorb the heat of the reaction.
An acid is a substance that reacts with a base. If you mix equal amounts of a strong acid and a strong base the two chemicals essentially cancel each other out and produce a salt and water. Acids are chemical compounds that show in water solution a sharp taste a corrosive action on metals and the ability to turn certain blue vegetable dyes red.
Mixing equal amounts of a strong acid with a strong base also produces a neutral pH pH 7 solution. Equimolar 001M and equivolume solutions of HCl and NaOH are combined to make salt water. Calculate the volume of the resultant solution after the acid and base are mixed together.
Mixing Acids and Bases Practice IV ACID-BASE TITRATION Chemistry 121 Hanson You know what a titration is we slowly add one solution to another. Then we study reactions of strong acids and. This is because a single molecule of H 2 SO 4 contains two acidic protons H Ions.
To summarise if we add 10 mL of 010 mol L-1 NaOH aq to 25 mL 010 mol L-1 CH 3 COOH aq the solution immediately after the completion of the neutralisation reaction is made up of 0043 mol L-1 CH 3 COOH aq and 0029 mol L-1 CH 3 COONa aq. A neutralization reaction is when an acid and a base react to form salt and water and it involves the combination of H ions 0H- to form water. The first scientific concept of acids and bases was provided by Lavoisier in around 1776.
One solution has one of the reactants of a chemical reaction. Vresultant solution Vacid Vbase Convert this volume to litres L if neccessary. Common acids found in the kitchen are lemons apple juice orange juice vinegar and black coffee.
Acetic acid is a weak acid some of the acetic acid in the beaker will dissociate to produce extra acetate ions and. Mixing Acids and Bases Practice II -- Chemistry 121A Hanson When we mix an acid and a base we expect a reaction. HCl H 2 SO 4 HNO 3 are some examples to strong acids.
The result is a perfectly balanced solution of salt and water with a pH of 7 if the acid and base are balanced properly. When mixed acids and bases neutralize one another and produce salts substances with a salty taste and none of the characteristic. Lavoisiers oxygen theory of acids.
A base is a substance that will neutralize an acid. They are usually identified as a sour tasting chemical. Mixing sulfuric acid and water is particularly risky because any splashed acid is corrosive enough to immediately burn skin and clothing.
Add the acid in small amounts of volume and stir thoroughly prior to adding more. We observed that mixing a strong acid and a strong base in equal amounts and concentrations produces a neutral solution and that mixing a strong base with a weak acid in equal amounts and concentrations produces a basic solution. When one of these is an acid and the other is a base we have an acid-base titration.
A 1 M solution of H 2 SO 4 will contain one mole of H 2 SO 4 in 1 liter of solution but if the solution is titrated with a base it will be shown to contain two moles of acid. The neutralization of a strong base and a strong acid has a PH of 7. A Identify the principal acidic and basic species being mixed.
Acidbase definitions Historic development. Learn more about strong acids and strong bases. It is so called because the acid neutralizes the base.
The other solution has the other. Chlorine gas is very toxic and if it is inhaled it can cause acute chlorine gas poisoning. B Write a net ionic equation leading to products conjugate acid and base.
HA BOH BA H 2 O heat.
These acids are so strong that they arent even considered conventional acids. The chemical formula for this is HSbf6.
/GettyImages-186818266-58d3548c3df78c5162d48e32.jpg) Name The Strong Acids And World S Strongest Acid
Name The Strong Acids And World S Strongest Acid
But a chemical that youve got around your house will stop it cold.

Strongest acid in the world. It is stronger than the hydrochloric acid but less than hydroiodic acid. Worlds Strongest Acid The worlds strongest acid is the superacid called fluoroantimonic acid HSbF 6. The worlds strongest acid.
The record-holder used to be fluorosulfuric acid HFSO 3 but the carborane superacids are hundreds of times stronger than fluorosulfuric acid and over a million times stronger than concentrated sulfuric acid. Hydrochloric acid is just a hydrogen chloride solution in the water therefore it is highly pungent. Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest acid in the world.
In mineral acids it is the strongest acid known. Sadly carborane is rather rare and likely wont be making a wide appearance in chemistry classes anytime soon. An acid when it hits water.
It means will be available for regular users on Thursday 11 February. Inside chemistry labs chemists work with what they call superacids. Concentrated sulfuric acid is already more than a billion times 10 12 stronger than dilute swimming pool acid or the acid in ones stomach.
There are different types of mixtures that are known to create what is considered to be superacids. The most common but strongest acid in the world. Whereas fluoroantimonic acid is actually is a mixed acid.
Various mixtures produce the superacid but the mixture of equal ratios of the two acids produces the strongest superacid known to man. No ones found a specific use for such a fantastically strong acid yet but chemists are. However theres still an ongoing debate as to whether carborane is the strongest of them all.
When hydrogen bromide is dissolved in water hydrobromic acid is formed. It is formed by mixing hydrogen fluoride HF and antimony pentafluoride SbF 5. The strongest one is at least a million times stronger than concentrated sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 and hundreds of times stronger than the previous record holder fluorosulfuric acid HFSO 3.
Carborane acids are the strongest known single-component acids on Earth far more acidic than the likes of perchloric and triflic acid. The strongest acid in the world is fluoroantimonic acid. Learn more information about strongest acid in the world.
It is 20 quintillion times more acidic than 100 sulfuric acid and it can dissolve glass plus a host of other substances. A strong superacid of this kind is fluoroantimonic acid. Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest super-acid known in existence.
The carborane superacids may be considered the worlds strongest solo acid as fluoroantimonic acid is actually a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and antimony pentafluoride. Another group of superacids the carborane acid group contains some of the strongest known acids. None of the strong acids traditionally listed in a chemistry text holds the title of Worlds Strongest Acid.
HCL is commonly used in the industrial sector naturally found in the gastric acid. Perhaps confusingly it is also one of the least corrosive. They are labelled superacids.
In other words fluoroantimonic acid donates protons around a billion times better than sulfuric acid. It is a solution of aqueous nature when boiling constantly and distills at a temperature of 1243oC and has 476 hydrogen bromide by weight. It is over a billion times stronger than pure sulfuric acid.
If you would like to read it just right now you must log in. Technically carborane is the worlds strongest solo acid because fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of antimony pentafluoride and hydrofluoric acid. Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest superacid based on the measured value of its Hammett acidity function H 0 which has been determined for different ratios of HFSbF 5.
HCL is its chemical formula. This can be created when hydrogen fluoride is mixed with antimony pentafluoride. It can rip through most materials easily.
The worlds strongest acid at least a million times more potent than concentrated sulphuric acid has been made in a lab in California. This article is marked as featured. The most powerful superacid in the world is fluoroantimonic acid HSbF 6.
Finally when treated with anhydrous acid zeolites microporous aluminosilicate minerals will contain superacidic sites within their pores. While the H 0 of pure HF is 15 addition of just 1 mol of SbF 5 lowers it to around 20. Carborane has a pH value of -18.
Fluoroantimonic acid is the worlds strongest acid proudly standing on the pedestal slightly above carborane. In this article well discuss strongest acid in the world. Unlike fluorosulfuric acid and fluoroantimonic acid the carborane acids are so noncorrosive that they may be handled with bare skin.
On the other hand glacial acetic acid is nothing but a pure or concentrated form of acetic acid. Removing the water from acetic acid lowers its melting point by 02 C.
Glacial Acetic acid is pretty much effective while producing ester.

What is glacial acetic acid. We can dilute this acid by adding water to prepare the required concentration of acetic acid solutions. Ethanoic Acid is commonly known as Acetic Acid. It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid.
How Glacial Acetic Acid Is Different. Although its mechanism of action is not fully known undissociated acetic acid may enhance lipid solubility allowing increased fatty acid accumulation on the cell membrane or in other cell wall structures. Glacial acetic acid is colourless and is very corrosive.
This acid is also called anhydrous acetic acid as it contains little amount of water. It can be synthesized by oxidizing acetaldehyde in the presence of manganese or cobalt salts. When acetic acid is at 995 percent concentration it is referred to as glacial acetic acid.
This acid is classified as a weak acid. Acetic acid that contains a very low amount of water less than 1 is called anhydrous water-free acetic acid or glacial acetic acid. What is Glacial Acetic Acid.
Glacial acetic acid is a trivial name for water-free anhydrous acetic acid. Anhydrous acetic acid can be transformed into a corrosive ice-like crystal at a temperature slightly lower than room temperature 167C. Acetic Acid is a synthetic carboxylic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties.
The acetic acid contains water. Acetic acid is considered an organic compound and has the chemical formula CH 3 COOH. It is frequently used as a solvent for recrystallization to purify organic compounds.
Glacial acetic acid is used in analytical chemistry for the estimation of weakly alkaline substance. Acetic acid also known as ethanoic acid is a clear colourless liquid which has a pungent vinegar-like odour. Feb 10 2021 The Expresswire -- Final Report will add the analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on this industry Global Glacial Acetic Acid Market has.
Although it is classified as a weak acid acetic acid is highly dangerous to skin. Solution for Pure acetic acid HC H3O2 is a liquid and is known as glacial acetic acid. Thus it has 100 acetic acid only.
Similar to the German name Eisessig ice vinegar the name comes from the ice-like crystals that form slightly below room temperature at 166 C 619 F the presence of 01 water lowers its melting point by 02 C. Glacial Acetic Acid Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard. Since it is too concentrated the acidity of glacial acetic acid is high.
Esterification is done along with the water in glacial acetic acid. It is a hygroscopic corrosive liquid with a vinegar-like odor. Glacial acetic acid is the undiluted form of acetic acid.
The reason its called glacial is because it solidifies into solid acetic acid crystals just cooler than room temperature at 167 C which ice. Acetic acid glacial 100 CAS 64-19-7 EMPROVE ESSENTIAL Ph EurBPJPUSPE 260 - Find MSDS or SDS a COA data sheets and more information. Glacial acetic acid is the anhydrous undiluted or free of water form of acetic acid.
The Glacial acetic acid is an eminent polar-base solvent and so that it has been used in the production of the followings. The experimental formula of Glacial Acetic Acid is CH2O and the chemical formula is C2H4O2. It doesnt contain any water.
It is utilized for synthesizing acetic anhydride cellulose acetate and acetic esters. Certified Reference Material Sorry we cannot compare more than 4 products at a time. Difference Between Acetic Acid and Glacial Acetic Acid.
A diluted solution of acetic acid is known as vinegar or ethanoic acid or ethylic acid. Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Glacial acetic acid is an excellent polar solvent.
Its impact on the degradation of historic paper has been. Acetic acid is an aliphatic organic acid. The acetic acid does not form crystals.
The glacial acetic acid does not contain water. Glacial acetic acid is a name for water-free acetic acid. When used as an herbicide the acetic acid can kill weeds that have emerged from the soil but does not affect the roots of the weed so they can regrow.
When it is pure 100 acetic acid it is referred to as glacial acetic acid. Therefore anhydrous acetic acid is often called glacial acetic acid. Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 25 00 ml of.
The pure anhydrous acetic acid forming ice-like crystals at temperatures below 167C is called glacial acetic acid.
Both formic acid and acetic acid are simple carboxylic acids. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant pKa value.
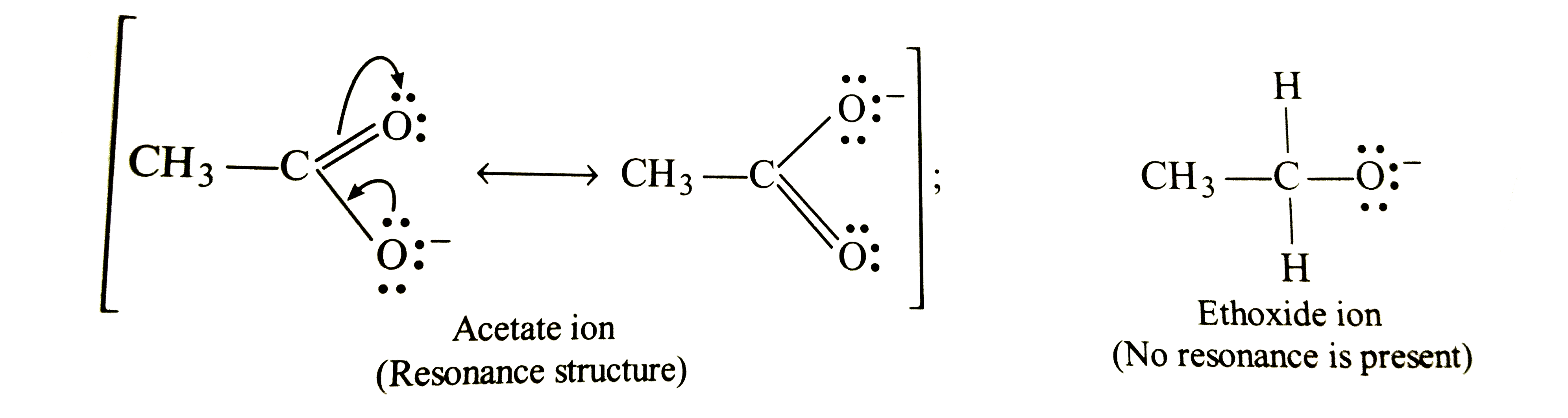 Explain A Acetic Acid Is A Stronger Acid Than Ethyl Alcohol Br
Explain A Acetic Acid Is A Stronger Acid Than Ethyl Alcohol Br
This works in its favor though.

Is acetic acid a strong acid. Weak Acid Acetic acid is a weak one because it fails to dissociate completely in aqueous solutions and does not release all its hydrogen ions. Although its mechanism of action is not fully known undissociated acetic acid may enhance lipid solubility allowing increased fatty acid accumulation on the cell membrane or in other cell wall structures. Among formic acid and phenol formic is stronger acid because.
For example in liquid ammonia acetic acid ionizes completely and may be considered a strong acid even though it is a weak acid in water. It then can be titrated using a solution in glacial acetic acid of a very strong acid such as perchloric acid. Moreover acetic acid has a pungent odor which is similar to the odor of the vinegar and a characteristic sour taste as well.
However formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid whereas acetic. Halogenation at alpha position increases acid strength so that the following acids are all stronger than acetic acid. The other strong acids are perchloric acid sulfuric acid nitric acid hydriodic acid hydrobromic acid etc.
Acetic acid is a versatile acidic solvent. However acidity and basicity have meaning in nonaqueous solvent. This formative assessment targets the question how does structure influence reactivity Students need to understand the behavior of strong and weak acids to comprehend phenomena like buffering capacity.
The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. Glacial acetic acid is the concentrated form of acetic acid. Acetic Acid is a synthetic carboxylic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties.
It is also a weak acid because it dissociates partially in aqueous solution releasing acetate anion and a proton. Acetic acid dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in both polar water and nonpolar hexane chloroform solvents. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid perchloric acid nitric acid and sulfuric acid.
Hence formic acid is strongest. Which furthermore indicates that acetic acid is weak because strong ions ionize almost completely. Acetic acid isnt a strong acid in the scientific sense its acid dissociation constant value is low.
This basically means that the ratio of CH3COOH concentration to the concentration of H and CH3COO ions is 1176 105. A weak acid is only partially dissociated with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present in solution in equilibrium with each other. By dissolving in water and being mixed with other chemicals it has incredibly broad applications.
Acetic acid is an example of a weak acid. Glacial acetic acid is used in analytical chemistry for the estimation of weakly alkaline substances such as organic amides. The key difference between formic acid and acetic acid is that formic acid or methanoic acid HCOOH contains a carboxylic acid group attached to a hydrogen atom whereas acetic acid or ethanoic acid CH 3 COOH has a methyl group attached to a carboxylic acid.
The strength of. HA H A. However acetic acid is not fully miscible with higher alkanes such as octane.
Lactic acid CH 3-CHOH-COOH Oxalic acid HOOC-COOH Tartaric acid HOOC-CHOH-CHOH-COOH Halogenated carboxylic acids. Acetic acid CH 3 COOH Citric acid C 6 H 8 O 7 Formic acid HCOOH Gluconic acid HOCH 2-CHOH 4-COOH. HCH3COO CH3COOH 176 105.
The delocalozation of negative charge after losing proton is more delocalized in formate ion on two oxygens whereas in phenoxide ion O being more electronegative will always have higher charge density even after ring delocalization. As a solvent acetic acid is a hydrophilic protic solvent much like water or ethanol. In How strong an acid is vinegar the students explore the nonlinear relationship between the concentration of a weak acid and the pH of the solution.
As with all chemicals be careful when you handle acetic acid. Glacial acetic acid is a much weaker base than water so the amide behaves as a strong base in this medium.
Examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine Prozac and the material PTFE Teflon. Meanwhile HF is a weak acid with a Ka value of eqrm66 times 10-4 eq.
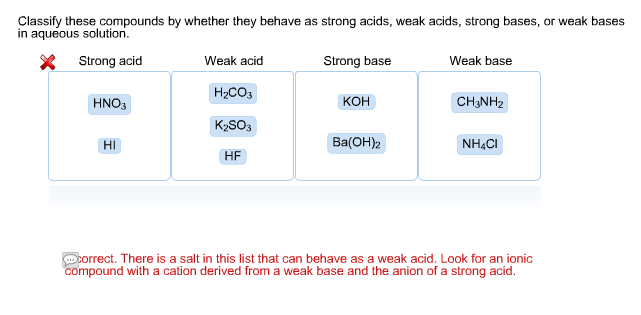 Solved Classify These Compounds By Whether They Behave As Chegg Com
Solved Classify These Compounds By Whether They Behave As Chegg Com
These acids are so strong that they arent even considered conventional acids.

Is hf a strong acid. Because of this HF and F are conjugate acid-base pairs where HF is a weak conjugate acid while F is a strong conjugate base. Classify each of the following acids as strong or weak. Acid is a substance which gives out H ions in aqueous solution.
In chemistry there are seven strong acids. Fluoroantimonic acid is the worlds strongest acid proudly standing on the pedestal slightly above carborane. The hydrogen-fluorine bonding HF is relatively strong so it only partially dissociates in water making it a weak acid.
The hydrogen-chlorine bond in HCl is very weak allowing it to completely dissociate in water thus qualifying it as a strong acid. However acidity and basicity have meaning in nonaqueous solvent. That is an aqueous solution of HF will contain many intact HF molecules and fewer F and H 3 O ions.
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride HF in waterSolutions of HF are colourless acidic and highly corrosiveIt is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon. Ill tell you the Acid or Base or Salt list below.
Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid HCl perchloric acid HClO 4 nitric acid HNO 3 and sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4. If the acid is weak write an expression for the acid ionization constant Kaa. Acid strength is the tendency of an acid symbolised by the chemical formula HA to dissociate into a proton H and an anion A The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete except in its most concentrated solutions.
However it is a weak acid and not a strong acid because it does not completely dissociate in water which is the definition of a strong acid or at least because the ions it forms upon dissociation are too strongly bound to each other for it to act as a strong acid. HF is a weak acid but very dangerous you may hear it etches glass thats because the SiF bond is the strongest bond. Hydrofluoric acid or HF is an extremely corrosive acid.
HA H A. Is Hf A Strong Acid. Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H FThis colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acidIt is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers eg.
In most applications strong acids are discussed in relation to water as a solvent. Acidity and Basicity of Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry. HF is widely used in the petrochemical.
The conjugate base of a strong acid is much weaker than water as a base. If you want to quickly find the word you want to search use Ctrl F then type the word you want to search. HCl is a strong acid because it completely dissociates when placed in water.
Elemental fluorine is produced from it. They are labelled superacids. However theres still an ongoing debate as to whether carborane is the strongest of them all.
What makes them strong is the fact that they completely dissociate into their ions H and an anion when they are mixed with water. In the case of strong acids the equilibrium strongly favors the product or is to the right of a chemical equation. Every other acid is a weak acidBecause there are only seven strong acids it is easy to commit the list to memory.
Thus weaker acids have stronger conjugate bases.
