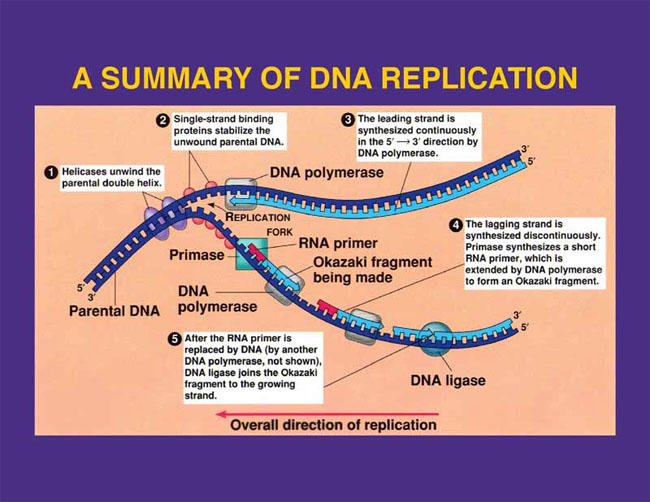
The first step in DNA replication is to unzip the double helix structure of the DNA molecule. Helicase opens up the DNA-forming replication forks.
Single-strand binding proteins coat the DNA around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of the DNA.

Describe the process of dna replication. This is carried out by an enzyme called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases of DNA together A with T C with G. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanceThis is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own. Replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes occurs by very similar mechanisms and thus most of the information presented here for bacterial replication applies to eukaryotic cells as well.
The three phases of replication process are. Read this article to learn about the three phases of DNA replication process. DNA replication is an important part of reproduction.
In DNA replication the genetic information is duplicated to produce two identical copies of the genome of an individual. DNA replication is a process in which the DNA divides into two same copies during cell division. This occurs at the cellular level leading to the multiplication of the genetic material.
The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows. The steps involved in DNA replication must happen in a precise order. DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single double-stranded DNA molecule.
It is bidirectional process. It implies that half of the DNA is conserved. It is an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
Each strand of the original molecule has remained intact as it served as the template for the synthesis of a complementary strand. Nucleotides matching the bases exposed by the unwinding base pair with their match. Supercoiled double-stranded DNA is relaxed by an enzyme called topoisomerase or gyrase and then unwound by an enzyme called helicase which opens up the two strands in one area at a time.
This DNA replication is a process that helps to transfer the genetic characters from parents to offspring. It uses energy obtained from ATP Hydrolysis to perform the function. DNA Replication is Semi-Conservative.
These templates are what will be the guide for the formation of the new strands. DNA unwinds at the origin of replication. Watson and Crick model suggested that DNA replication is semi-conservative.
The three steps in the process of DNA replication are initiation elongation and termination. DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme in the replication process. Helicase The point at which the replication begins is known as the Origin of Replication.
Describe the process of DNA replication including the role of the origins of replication and replication forks. The purpose of DNA replication is to create two daughter DNA molecules which are identical to the parent molecule. Helicase brings about the procedure of strand separation which leads to the formation of the replication fork.
The replication occurs in three basic steps as. It is a biological polymerization which proceeds in the sequence of initiation elongation and termination. In the process of DNA replication the DNA makes multiple copies of itself.
Replication begins at specific sites origins where two parental strands separate to form replication bubbles. DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. Here are the major steps involved in DNA replication.
Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. That is each. Three basic steps involved in DNA replication are Initiation elongation and termination.
During DNA replication the two parental strands separate and each acts as a template to direct the enzyme catalysed synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand following the normal base pairing rule. These are extended in both directions. Antiparallel structure refers to the orientation of each strand in.
DNA replication is fundamental process occurring in all living organism to copy their DNA. In molecular biology DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. 1 Initiation 2 Elongation and 3 Termination.
The process of DNA replication makes a duplicate copy of a DNA strand to be separated in cell division. Step 1 The protein Helicase splits the double stranded DNA molecule forming two single stranded templates. The process whereby the DNA duplicates to produce new ones is known as DNA Replication.
The process is called replication in sense that each strand of ds DNA serve as template for reproduction of complementary strand. DNA Replication is Semiconservative When the replication process is complete two DNA molecules identical to each other and identical to the original have been produced. General feature of DNA replication.
DNA replication is semi conservative. The DNA copied accurately in the daughter cells. It breaks the hydrogen bond between the base pairs to separate the strand.
Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand.