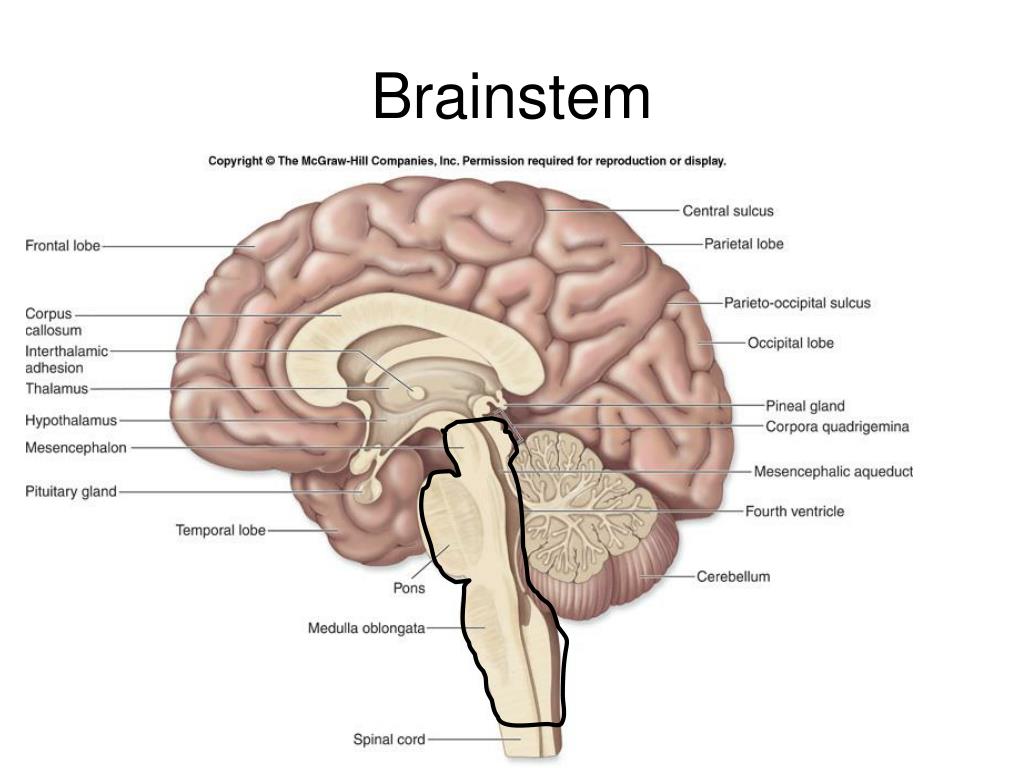
The brainstem consists of three parts. The midbrain the pons and the medulla oblongata.
 Ppt Human Anatomy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 762904
Ppt Human Anatomy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 762904
The brainstem consists of the medulla oblongata pons and midbrain.

The brainstem consists of the. The brain stem controls the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body and it also controls basic body functions such as breathing swallowing heart rate blood pressure consciousness and whether one is awake or sleepyThe brain stem consists of the midbrain pons and medulla. The name comes from the Greek mesos middle and enkephalos brain. The brainstem is made up of all the unpaired structures that connect the cerebrum with the spinal cord.
Just the two cerebral hemispheres there are also a right and a left cerebral peduncle. Key Terms pons. The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision hearing motor control sleep and wakefulness arousal alertness and temperature regulation.
In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain the pons and the medulla oblongata. The brainstem is a very small component of the brain making up only around 26 percent of its total weight. Together they help to regulate breathing heart rate blood pressure and several other important functionsAll of these brainstem functions are enabled because of its unique anatomy.
The brainstem refers to the middle part of the brain 1It consists of the medulla pons and midbrain. It has the critical role of regulating cardiac and res. The function of the brainstem is to control the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The brainstem also has known as brain stem is the back part of the brain joining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. These functions are possible because of the brainstems unique anatomy 3. The brain stem performs the motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck through the cranial nerves.
The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. Floor of the fourth ventricle and. The brainstem is sometimes called the reptilian brain since it is the oldest and most fundamental structure in the brain.
These structures are the epithalamus the thalamus the hypothalamus and the subthalamus. The brainstem brain stem is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain pons and medulla oblongataEach of the three components has its own unique structure and function. The brainstem or Truncus encephali in Latin is a brain structure located between the medulla and the spinal cord 1.
It is the base of the brain. The brainstem is the region of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. It consists of the midbrain medulla oblongata and the pons.
Most cranial nerves are found in the brainstem. The stem-like part of the base of the brain that is connected to the spinal cord. Motor and sensory neurons travel through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and the spinal cord.
The brainstem is the structure that connects the cerebrum of the brain to the spinal cord and cerebellum. The brainstem consists of the medulla oblongata pons and midbrain. It is composed of 3 sections in descending order.
Midbrain mesencephalon pons part of the metencephalon medulla oblongata myelencephalon The brainstem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Dorsal columns the 2. It adjoins is structurally continuous with the spinal cord and consists of the.
The brain stem regulates autonomic function respiration circulation lacrimation salivation controls visual and auditory reflexes and maintains vigilance. The brainstem comprises three components. The brainstem is the posterior part of the brain continuous with the spinal cord.
The brainstem helps relay sensory information such as pain eye and mouth movement involuntary muscle movements consciousness respirations hunger and cardiac function 2. It is responsible for many vital functions of life such as breathing consciousness blood pressure heart rate and sleep. The brain stem is the caudal part of the brain and consists of the midbrain pons and medulla oblongata.
The midbrain is the most superior portion of the brainstem connecting the brainstem to the cerebrum by the cerebral peduncles not to be confused with the cerebellar peduncles which connect the brainstem to the cerebellum. The midbrain pons and medulla oblongata. In the brain brainstem comprises the midbrain the pons and the medulla oblongata.
Contains nuclei that relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum along with nuclei that deal primarily with sleep respiration swallowing bladder control hearing equilibrium taste eye movement facial expressions facial sensation and posture. Dorsal aspect of the brain stem consists of the dorsal columns the floor of the fourth ventricle and the superior and inferior colliculi. The brainstem is the most caudal part of the brain.
The brainstem also plays an important role in the regulation of cardiac and respiratory function consciousness and the sleep cycle. Most rostral in the brainstem are structures often collectively referred to as the diencephalon. It consists of the midbrain the medulla oblongata or the long medulla the Varolis bridge and the spinal cord.
Mesencephalon midbrain pons and medulla oblongata. Since the brainstem. Sometimes the diencephalon which is the caudal part of the forebrain is also included.
Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules. One or more phosphate groups.
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png) 3 Parts Of A Nucleotide And How They Are Connected
3 Parts Of A Nucleotide And How They Are Connected
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate.

A nucleotide consists of. Similarly when the sugar is deoxyribose a nucleotide is a deoxyribonucleotide and is used for the biosynthesis of DNA. While forming a DNA molecule deoxyribose acts as a specific sugar. What does a nucleotide consist of.
Nucleic acids consist of a chain of linked units called nucleotides. This phosphate is important in the formation of phosphodiester bonds which link several nucleotides in a linear fashion. Nucleotide is a basic building unit of DNA.
A nucleotide consists of. A nucleotide consists of three things. A nucleotide is made up of the following Sugar ring base adenine guanine cytosine thymineuracil phosphate molecule.
A nucleotide is made up of three parts. What does the term nucleotide refer to. The second part of a nucleotide is the phosphate which differentiates the nucleotide molecule from a nucleoside molecule.
When the nucleotides are linked together they are supported by the phosphate bond and sugar as backbone. A five-carbon sugar a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. A phosphate group a 5-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base.
A nucleotide consists of what three parts. RNA and DNA are polymers made of long chains of nucleotides. 2a sugar a base and a phosphate.
Nucleotide consists of A phosphate only B phosphate and sugar only C phosphate sugar and nitrogen base D phosphate and nitrogen. A nucleoside doesnt have a phosphate. A phosphate group and a sugar ribose in the case of RNA deoxyribose in DNA make up the backbone of the nucleic acid strand and attached to the sugar is one of a set of nucleobasesThe nucleobases are important in base pairing of strands to form higher-level secondary and.
J K CET 2007. Nucleotide consists of A phosphate only B phosphate and sugar only C phosphate sugar and nitrogen base D phosphate and nitrogen. A phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
The third part of a nucleotide is the pentose 5 carbon sugar. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous basepentose-phosphate.
A nitrogenous base which can be either adenine guanine cytosine or thymine in the case of RNA thymine is replaced by uracil. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleotides that have adenine or.
All of the above. A nucleotide consists of A carbon sugar B nitrogen containing base C phosphoric acid D All of these. They also have functions related to cell signaling metabolism and enzyme reactions.
When the sugar is ribose a nucleotide is a ribonucleotide and is used for the biosynthesis of RNA. In both DNA and RNA a nucleotide consists of three parts. Each nucleotide consists of three subunits.
The bases used in DNA are adenine A cytosine C guanine G and thymine T. Check Answer and Solution f. What does a nucleoside consist of.
Draw a general nucleotide see figure 331 for help ask Meza if you are unsure which. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth.
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine cytosine guanine and thymine. A nucleobase a five-carbon sugar and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. A nucleotide consists of base sugar and phosphate group.
A five-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base a pentose sugar and a phosphate group. The sugar ring is made up of carbon atoms.
In RNA the base uracil U takes the place of thymine. A sugar and a phosphate. Nitrogenous bases are the complex heterocyclic ring structure which includes adenine guanine cytosine and thymine bases in DNA and uracil is present instead of thymine in RNA.
A nucleotide consists of. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside. Each nucleotide comprises of three major constituents a A sugar b A phosphate and c a nitrogenous base.
J K CET 2007. Nucleotide consists of - Tardigradein. 3a sugar a base and three phosphates.
A nucleotide consists of. A nitrogenous base simply called a base in the context of biochemistry is an organic molecule that contains nitrogen. Sugar nitrogenous base phosphate.
A five-carbon sugar called deoxyribose because it is lacking an oxygen group on one of its carbons.