Therefore they will have the same type of bonding and forces influencing them. Water has a very high specific heat capacity of 41814 JkgK at 25 C the second-highest among all the heteroatomic species after ammonia as well as a high heat of vaporization 4065 kJmol or 2257 kJkg at the normal boiling point both of which are a result of the extensive hydrogen bonding between its molecules.

Therefore the boiling point of H₂S should be less than 300K.
Boiling point of h20. Boiling point elevation equation. Therefore our next course would be looking at the molecular. MgBr2s H20 -- Mg2 aq 2Br- aq Chemistry.
This approximation is sufficient for this kind of calculations. 100 low impact 20 minute total body workout. This boiling point calculator finds the pressure at altitude assuming that the pressure at sea level is constant and equal to 1013 hPa 1013 bar.
The melting point and freezing point of water ideally are the same especially if there are gas bubbles in water but if the water is free of nucleating points water can supercool all the way down to 42 C 436 F 231 K before freezing. Hydrocarbons alcohols and acids - boiling points - Boiling temperature C and F with varying carbon number up to C33 Ice Water - Melting Points at Higher Pressure - Online calculator figures and tables showing melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia 0 to 2000 bara. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure.
Therefore the correct option is 2 Prev Question Next Question Related questions 0 votes. And we aint got no data here. During boiling one has to break the bonds and hence greater amount of energy is required in case of H20 since it is more stable and thus it has a higher boiling point.
1 Greater than 300 K but less than 373 K. The boiling of water 373 K is abnormally high when compared to that of H2S 2112 K. Physical-chemistry intermolecular-forces hydrogen-bond phase.
You should look up the boiling points on the web or in your text and then you should try to rationalize them on the basis of intermolecular or interparticle force. Workout 5 of 5 H20 Plan. The boiling point of water depends on the atmospheric pressure which changes according to elevation.
H2O HF NH3 CH4. Which has the highest boiling point. H20HFNH3 in that order although I assume youre really looking for the explanations here.
So in some cases the melting point of water is considerably higher than its freezing point. It has a role as an amphiprotic solvent a member of greenhouse gas a human metabolite a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. The given substances according to their increasing boiling points can be arranged as.
Order of increasing boiling point stackrelrarrN_2 HCl H_2O NaCl But a scientist interrogates data. So what is an explanation for the difference in boiling point between hydrogen fluoride and ammonia. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure.
Compare the amount of heat required to vaporize a 200-gram sample of H20L at its boiling point to the amount of heat required to melt a 200-gram sample ofH20s at its melting point. It is obvious that will have the highest boiling point as it has hydrogen bonding. The remaining compounds like have the same group in the periodic table.
Hydrogen bond is more strong than Van Der Waals ForcePresent in H2S so H20 is more stable. Water is an oxygen hydride consisting of an oxygen atom that is covalently bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Water boils at a lower temperature as you gain altitude eg going higher on a mountain and boils at a higher temperature if you increase atmospheric pressure coming back down to sea level or going below it.
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. If the boiling point of H2O is 373 K the boiling point of H2S will be. H2O has the highest boiling point due to its ability to form 2 hydrogen bonds per molecule.
Write the equation for the dissolution of magnesium bromide in water. These two unusual properties allow water to moderate Earths. Remember that the boiling point of water depends solely on pressure.
Boiling point of fluoride is 195 degrees Celsius while boiling point of ammonia is minus 33 degrees Celsius which makes 535 degrees difference.
With the help of this knowledge one can also conclude that the freezing point formula is. It is a colligative property of solutions that is generally proportional to the molality of the added solute.

The following equation is used to calculate the freezing point of a liquid.
Freezing point depression formula. LatexDelta T_f itimes K_f times molalitylatex In this equation latexDelta T_flatex is the freezing point depression Kf is the freezing point depression constant and i is the van t Hoff factor. DT f is the freezing point depression. Since the vapour pressure of a solution is less than that of pure solvent the freezing point of the solution will be lower than that of.
The freezing point depression can be calculated by the formula. It is observed that the freezing point of a solution is always less than the freezing point of the pure solvent. This kind of measurement is called cryoscopy Greek cryo cold scopos observe.
DT iK f m where DT Change in temperature in C i van t Hoff factor K f molal freezing point depression constant or cryoscopic constant in C kgmol m molality of the solute in mol solutekg solvent. Density of water at 35 C 0994 gmL K f water 186 C kgmol Solution. Formula For Depression in Freezing Point Chemistry Formulas.
We can now find the molecular weight of the unknown compound. Where DT Temperature change celsius i Vant hoff factor K f Cryoscopic constant kgmol. Freezing point is a temperature at which a solid and a liquid state of a substance have the same vapour pressure.
Thus by the knowledge of the Freezing Point Depression Coefficient one can easily obtain the freezing. DT f is the freezing point depression i is the vant Hoff factor Kf is the molal freezing point depression constant for the solvent and. Kf is the freezing point depression constant.
An equation has been developed for this behavior. Illustrating freezing point depression Students in groups of two or three can observe freezing point depression through the making of ice cream. Dt i K f m.
Freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of solvents upon the addition of solutes. T K f m. Observe the cold 4 and relies on exact measurement of the freezing point.
Depression in Freezing Point. Examples include salt in water alcohol in water or the mixing of two solids such as impurities in a finely powdered drug. Since saltwater will freeze at colder temperatures organisms can survive in these bodies of water.
Freezing-point depression describes the process in which adding a solute to a solvent decreases the freezing point of the solvent. This is the colligative property called freezing point depression. Molecular Weight 200 g u n k n o w n 000923 m o l 21680 g m o l.
Freezing Point total Freezing Point solvent - DT f. Both the boiling point elevation and the freezing point depression are related to the molality of the solution. The formula to calculate freezing point depression is.
The freezing point depression is the amount the freezing temperature decreases. DTf i x kf x m In this freezing point depression formula DTf is the freezing point depression i is the Vant Hoff factor kf is the cryoscopic constant and m is the molality. The formula for freezing point depression expression is.
Thus the amount of depression depends on the amount of solute added into the solution ie depends on the molarity M of the solution. The freezing point may be defined as the temperature at which the liquid and solid states of a substance have the same vapor pressure. The Freezing point depression takes place when we add a new compound into the liquid to reduce its freezing point.
Mole depression constant - formula Mole depression constant. Looking at the formula for the boiling point elevation and freezing point depression we see similarities between the two. The depression in the freezing point of a solution can be described by the following formula.
A a DT f iKfm a a. Freezing Point Depression Formula Freezing point depression can be calculated using the Clausius-Clapeyron equation and Raoults law. Freezing point depression the freezing point goes down occurs when solute is added to the pure solvent.
To find the temperature change elevation of a solvent by a solute use the freezing point depression equation. This is the freezing point lowering effect. The materials required and procedures are as follows.
The more solute dissolved the greater the effect. M is the molality of the solution. Where T is the freezing point.
K f R T 2 1 0 0 0 L. Freezing point depression is the decrease of the freezing point of a solvent on the addition of a non-volatile solute and is represented as DTfKfm or Freezing point depressionMolal freezing point constantMolality. DT f iK f m.
The freezing point depression is especially vital to aquatic life. Dt is the temperature change from the pure solvents freezing point to the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression constant changes depending on the solvent and the van t Hoff factor accounts for the number of particles that a dissolving solute creates in solution.
Materials per group of two or three small Ziploc bag 165 cm x 149 cm. In a dilute ideal solution the freezing point is. With the formula below freezing-point depression can be used to measure the degree of dissociation or the molar mass of the solute.
This is termed as the depression in freezing point of a solution.
We are giving a detailed and clear sheet on all Physics Notes that are very useful to understand the Basic Physics Concepts. Triple point of water.
 Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances
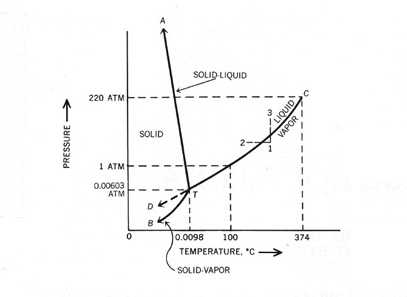
Point A is triple point where all three physical states of matter co exist.

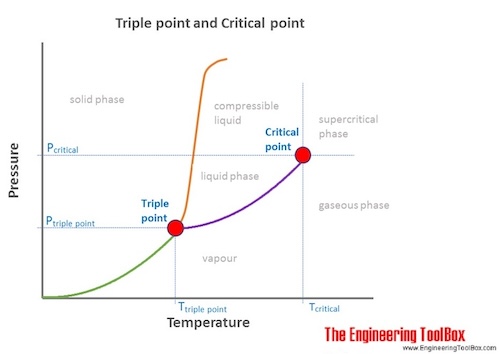
Triple point definition chemistry. Describe what one would see at pressures and temperatures above 5 atm and 1000C. The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid solid and gaseous states. It is a specific case of thermodynamic phase equilibrium.
The values of pressure and temperature at which water coexists in equilibrium in all three states of matter ie. A substance is said to be at its critical point when the absolute temperature associated with it is equal to its critical temperature and the pressure applied to it is equal to its critical pressure. It describes a specific thermodynamic state of matte.
The term triple point was coined by James Thomson in 1873. The term triple point was coined in 1873 by James Thomson brother of Lord Kelvin. Critical Point Definition.
The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid solid and gaseous states. For example the triple point of Acetylene occurs at -807 Celsius. Ice water and vapour is called triple point of water.
Sometimes the triple point may involve more than one solid phase when there are polymorphs of the substance exist. For example the triple point temperature of mercury is at 388344 C at a pressure of 02 MPa. The number given for the temperature of the triple point of water is an exact definition rather than a measured quantity.
The triple point of pure water is at 001C 27316K 3201F and 458 mm 6112Pa of mercury and is used to calibrate thermometers. The triple point of water is the point where one is interested in all three phases of water at a certain pressure and temperature. Triple Point The three-phase equilibrium lines meet at one point.
The value of the triple point of water was fixed by definition rather than measured but that changed with the 2019 redefinition of SI base units. The triple point of water is used to define the kelvin the SI base unit of thermodynamic temperature. Watch how water behaves at the triple point where it co-exists in solid liquid and vapour form.
1-solid 2-liquid 3-gas 4-supercritical fluid point O-triple point C-critical point -785 C The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -785 C 2. Meaning pronunciation translations and examples. In physics and chemistry the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which three phases gas liquid and solid of that substance may coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Triple point of water synonyms Triple point of water pronunciation Triple point of water translation English dictionary definition of Triple point of water. Chemistry chem the temperature and pressure at which the. Rank the states with respect to increasing density and increasing energy.
This triple point is the point where the temperature and pressure conditions are right for all three states solid liquid and gas. The critical point is the end point of a phase equilibrium curve defined by a critical pressure T p and critical temperature P cAt this point there is no phase boundary. The triple points of several substances are used to define points in the ITS-90 international temperature scale ranging from the triple point of hydrogen 138033 K to the triple point of water 27316 K 001 C or 32018 F.
The temperature and pressure at which a substance co-exist in thermodynamic equilibrium with its three physical states solid liquid gas is know as triple point. The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which it can exist in all three states. This experiment demonstrates the triple point of a substance.
The triple point of water occurs at an external pressure of 18 in and a temperature of 3202F In strict terms this process is desiccation not lyophilization because water removal is done at temperatures above the triple point of water Is there a formula to calculate the triple point of a substance. The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid liquid and vapour phases of a particular substance coexist in equilibrium. In a phase diagram The critical point or critical state is the point at which two phases of a substance initially become indistinguishable from one another.
In chemistry and physics the triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid liquid and vapor phases of a particular substance coexist in equilibrium. The temperature and pressure at which the three phases of a substance are in equilibrium. What Is Triple Point.
Triple Point of Water Definition. The triple point is a Thermodynamic Phenomenon It is a point where an element exists in Solid Liquid and Gaseous form and in Thermodynamic Equilibrium.
Triple point of water The precise conditions of pressure and temperature at which water coexists in its three phases in equilibrium - liquid water ice and vapor - occur at a temperature of exactly 27316 K 001 C and a partial pressure of steam. For example mercury it is at a temperature of 3883440 C and a pressure of 02 m Pa.
The triple point of pure water is at 001 degrees Celsius and 458 millimeters of mercury and is used to calibrate thermometers.
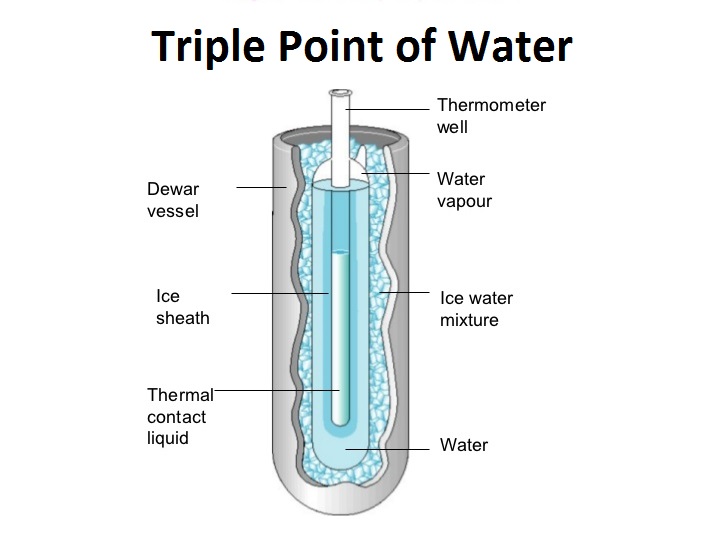
Triple point of water. The term triple point was coined in 1873 by James Thomson brother of Lord Kelvin. This agreement also sets the size of the kelvin as 127316 of the difference between the triple-point temperature of water and absolute zero. This is equivalent to 001oC and 3202oF and thus we use T3 to help set the freezing point of water.
The triple point pressure of water is the minimum pressure at which the water can exist as a liquid. Definition Thermometry and Calorimetry. The triple point of each pure substance is different.
Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. Thermal properties of matter. This was obtained with a standard vacuum pump.
Similarly the triple point of CO2 lies at 5660 C and 517 kPa. The triple point of water T 3 27316 K is the standard fixed-point temperature for the calibration of thermometers. Note that the triple point of water is 27316 K 001 C slightly above the normal freezing point.
Triple point of water is 273 K temperature and 046 cm of mercury pressure. Solution for The triple point of water is _____ a 27316C b 27316K c 27316F d 015K. Sometimes the triple point may involve more than one solid phase when there are polymorphs of the substance exist.
The triple point of water T 3 27316 K is the standard fixed-point temperature for the calibration of thermometers. This agreement also sets the size of the kelvin as 127316 of the difference between the triple-point temperature of water and absolute zero. Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit scales Kelvin is not measured using degrees.
The triple point of water is a standard fixed point in modern thermometry. The triple point is the temperature and pressure at which solid liquid and vapour phases of a particular substance coexist in equilibrium. 611656 pascals 000603659 atm.
The Mathematics of Triple Point. The triple point of water T 3 27316 K is the standard fixed-point temperature for the calibration of thermometers. Phase diagram of water will locate one point in curve at which all phases of water will coexist together.
The triple point of water TPW is the unique physical state of water in which all three phases solid liquid and v apour coexist at t hermodynamic equilibrium. The phase diagram of water is a pressure-temperature diagram for water that shows how all three phases solid liquid and vapor may coexist together in thermal equilibrium. Boiling point or vaporisation temperature of water is 373 K.
1 Answer 1 vote. For those water systems whose pressure is below the triple point pressure of water sublimation occurs. Triple point of any substance is that temperature and pressure at which that substance can co-exist in all three phases solid liquid and gas in equilibrium the triple point of water is 27316 K at 6112 Pa.
At triple point pressure will be 458 mm of Hg and respective temperature will be 000750C. The triple points of several substances are used to define points in the ITS-90 international temperature scale ranging from the triple point of hydrogen 138033 K to the triple point of water 27316 K 001 C or 32018 F. The triple point of water is defined to take place at 27316 K where K is the SI unit Kelvin.
The temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist in equilibrium in the liquid solid and gaseous states. We can see triple point in above phase diagram of water. The triple point of water was once used to define sea level on Mars.
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. What is Triple Point of Water. Answered 22 hours ago by Badiah 47k points selected 22 hours ago by Ekaa.
Triple Points substance Temp K Pressure kPa water 27316 0612 CO22166 518 nitrogen 6315 1246 data are from Zemansky and Dittman Heat and Thermodynamics7thed. This agreement also sets the size of the kelvin as 127316 of the difference between the triple-point temperature of water and absolute zero. It describes a specific thermodynamic state of matte.
A petri dish with sulfuric acid is also included under the Bell Jar to serve as a sink for all the high energy. We merely say Kelvin The triple point of water is important enough to merit its own line. The triple point of water is also used in sealed cells as pressure transfer standards.
The phase diagram of water is a pressure-temperature diagram for water that shows how all three phases solid liquid and vapor may coexist together in thermal equilibrium.
Water Boiling Points at Higher Pressure - Online calculator figures and tables showing boiling points of water at pressures ranging from 147 to 3200 psia 1 to 220 bara. For instance almost everyone knows that the freezing point of water is 0 degrees Celsius and the boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius.
Pure water - microscopic view.
Boiling point of pure water. Thus we dont use the degree symbol when reading temperatures in this system. It varies from 72C to 101C accordingly from the highest point to the lowest point on land. The IUPAC recommended standard boiling point of water at a standard pressure of 100 kPa 1 bar is 9961 C 2113 F.
The Boiling Point of Pure Water at 1 ATM is 212oF or 100oC Why pure water is less time to boil than water with salt. There are two conventions regarding the standard boiling point of water. The boiling point of water varies at various locations.
The output temperature is given as C F K and R. 10 M NaCl solution - microscopic view. Choose the actual unit of pressure.
Example 1383 In Example 1381 we calculated that the vapor pressure of a 302 aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at 100C is 851 mmHg less than the vapor pressure of pure water. The simple answer to this question is that the boiling point of water is 100 C or 212 F at 1 atmosphere of pressure sea level. Pressure must be within the ranges 0-1000 mbara 0-147 psia 0-760 mm Hg or 0-30 in Hg.
The calculator below can be used to calculate the water boiling point at given absolute pressures. Normal boiling point 1000 o C. We dont insert the degree symbol o or the word degree to refer to a specific temperature on the Kelvin scale.
Temperature given as C F K and R. The water vapour will also condense. In this regard the boiling point of water changes with a change in barometric pressure.
Boiling water is characterized by energetic bubbles and steam and it is considered to be hot. The boiling point of a liquid varies according to the applied pressure. The boiling point of water on the Kelvin scale is 3732 K.
However there is no danger of boiling the NaCl. For pure water the boiling point is 100 degrees Celsius 212 Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure and the melting point is 0 degrees Celsius 32 degrees Fahrenheit at one atmosphere of pressure. Hydrocarbons alcohols and acids - boiling points - Boiling temperature C and F with varying carbon number up to C33.
At sea level water boils at 100 C 212 F. If you boiled all the water off the ions would recombine to form solid salt. Pure water will melt at 0C and boil at 100C.
Boiling Point of NaCl. At at high altitudes the lower pressure makes the boiling point several degrees lower. Conventionally the temperature at which water boils is 100 degrees Celsius or 212 Fahrenheit but only at sea level.
The normal boiling point is 9997 C 2119 F at a pressure of 1 atm ie 101325 kPa. When you dissolve salt in water it breaks into sodium and chloride ions. Boiling and freezing points of pure substances are well-known and easily looked up.
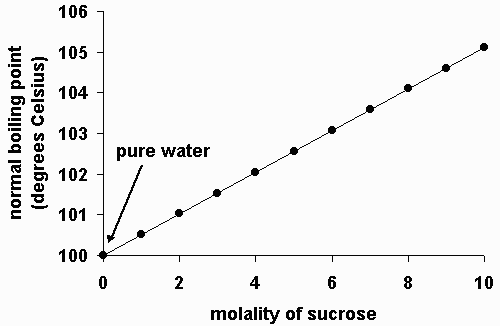
Whenever a solute such as salt is added to a solvent such as water the boiling point becomes higher than that of the pure solvent. The normal boiling point is the temperature at which the vapour pressure is equal to the standard sea-level atmospheric pressure 760 mm 2992 inches of mercury. However the value is not a constant.
The boiling point of water depends on the atmospheric pressure which changes according to elevation. Adding salt to water increases the boiling point of water due to a fundamental colligative property of matter known as boiling point elevation. Hence a 100 m NaCl solution will have a boiling point of about 10102C.
Testing its boiling point. For example the boiling point of pure water at 10 atm is 100 o C while the boiling point of a 2 saltwater solution is about 102 o C. The boiling point of pure water is lower than the boiling point of a.
The freezing point depression is the amount the freezing temperature decreases. It is important to recognize just how much the temperature of boiling water is reduced as the altitude increases. A lower boiling point means that food cooks at a lower temperature despite the fact that the water is boiling.
Every degree unit on the Celsius scale is equal to one degree unit on the Kelvin scale. Salt like other ionic solids has an extremely high boiling point. Pure substances have precise melting and boiling points.
Normal boiling point 1010 o C. The reason for these variations is the lowering of atmospheric pressure as we travel to the highest point such as mountains from lowest land point ie Dead sea. The boiling point of sodium chloride is 2575 F or 1413 C.
Therefore the boiling point elevation would be 2 o C. Note that the ionic solid NaCl produces Na ions blue and Cl-ions green when dissolved in water.