Hence the name potential energy. Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects.
 Types Of Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
Types Of Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
Following are a few examples of radiant energy.
Forms of energy examples. Examples of these are. When you stretch or compress a spring you are storing energy in the bonds between the springs metal atoms. Potential energy takes many forms like mechanical gravitational elastic chemical electric nuclear and magnetic potential energy.
Electromagnetic energy or radiant energy is energy from light or electromagnetic waves. When energy is stored in an object it has the potential to be used. The chemical energy from food can also be converted to thermal energy to keep the body warm.
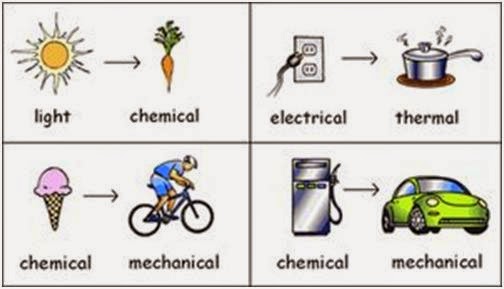
There is visible light and heat that is generated. Depending on the origin of the energy sources we distinguish the following types. Examples of energy transformation include generating electric energy from heat energy via a steam turbine or lifting an object against gravity using electrical energy driving a crane motor.
These shapes can be transformed into each other. A tensioned device such as a bow or spring though at rest has the potential for creating motion. There are various forms of potential energy depending on the kind of forces involved such as gravitational potential energy chemical potential energy electrical potential energy magnetic potential energy and nuclear potential energy.
Commercial grade wind-powered generating systems can power many different organizations while single-wind turbines are used to help supplement pre-existing energy organizations. The second form is vibrational kinetic energy which is generated due to the movement of vibrations. It contains potential energy because of its configuration.
Sunlight is an example of radiant energy. The phenomenon we call wind is caused by the differences in temperature in the atmosphere combined with the rotation of Earth and the geography of the planet. Examples are energy released by fission and fusion.
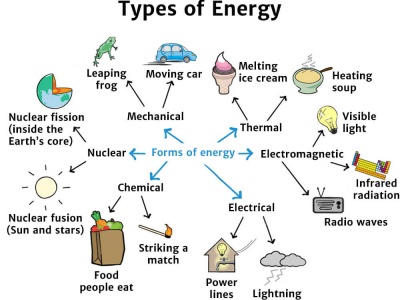
Energy can come in various forms. See more ideas about science 4th grade science physical science. All forms of energy are associated with motion.
Other forms of energy may include geothermal energy and classification of energy as renewable or nonrenewable. The forms of kinetic energy are. Chemical energy from food is converted to mechanical energy when the food is broken down and absorbed in the muscles.
Think about the air in a balloon when holding the end. It is the principle of conservation of energy. Lifting against gravity performs mechanical work on the object and stores gravitational potential energy in the object.
Its energy source is unlimited. Forms of energy are just different types of energy such as heat light sound kinetic and chemical. Technically wind energy is a form of solar energy.
Light energy heat energy mechanical energy gravitational energy electrical energy sound energy chemical energy nuclear or atomic energy and so on. As objects move faster more energy is stored. Forms of Kinetic energy.
Any form of light has electromagnetic energy including parts of the spectrum we cant see. Nuclear Energy - This is energy from interactions with the protons and neutrons of an atom. For example any given body has kinetic energy if it is in motion.
Jan 1 2021 - Explore Stephanie Betzs board Science Forms of Energy followed by 109 people on Pinterest. Energy resources are stores of a particular type of energy. Examples include chemical potential energy in your muscles or.
Examples of motion energy include wind a flowing river a moving car or a person running. The first form is rotational kinetic energy the energy that is produced due to rotational motion. Examples of energy resources.
Both these generated energies are a form of radiant energy. There are different types of energy depending on their effects and also on their origin. Each form can be converted or changed into the other forms.
Radio gamma rays x-rays microwaves and ultraviolet light are some examples of electromagnetic energy. Typically this relates to the strong force. For example a ball dropped from a height is an example of a change of energy from potential to kinetic energy.
When you turn on an incandescent light bulb it gives off two forms of energy. For example a crawling child a rolling ball a falling ball all possess some form of kinetic energy. Another form is utility-scale wind farms which are purchased by contract or wholesale.
Energy exists in many different forms. In more explicit words it is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. The third is translational kinetic energy the energy produced due to the motion from one location to another.
Another type of energy which can be stored easily.
Energy sublevels are contained within principal energy levels and their number increases as the value of. These numbers are the Principal Quantum Numbers.
 Can Any Elements Go Beyond The 5th Principal Energy Level Explain Why Or Why Not Brainly Com
Can Any Elements Go Beyond The 5th Principal Energy Level Explain Why Or Why Not Brainly Com
Energy of the stationary state in which an electron is placed is given by.
What is a principal energy level. Principal energy levels are an atoms major energy levels ranging in value from 1 to 7. A principal energy level may contain up to 2n 2 electrons with n being the number of each level. The third can contain up to 23 2 or 18 electrons and so on.
So our electron will fall back down to the ground state and give up four eV of energy. There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s p d and f sharp principle diffuse and fundamental. The second can contain up to 22 2 or eight electrons.
True or false. The formula for determining the number of electrons is two multiplied by n squared or 2n2. For the first principal energy level having two electrons in it is the most stable arrangement while for all other levels outside of the first eight electrons are necessary to achieve the most stable state.
The s - Sublevel can hold a maximum of. Once the electrons at the higher energy level it wont stay there long. The energy levels in the hydrogen atom depend only on the principal quantum number n.
Yes the 5th energy level holds 5 sublevels and that last one would be 5g. The p - Sublevel can hold a maximum of. The second principal energy level can have 8 the third can have 18 and so on until all 79 electrons have been distributed.
Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitals. The first energy level can contain 21 2 or two electrons. For a given n all the states corresponding to l 0 n 1 displaystyle l0ldots n-1 have the same energy and are degenerate.
The Orbitals are named K L M N or 1 2 3 4 in ascending order. For the bond in the molecule to be stable the covalent bonding electrons occupy the lower energy bonding orbital which may be signified by such symbols as s or p depending on the situation. The second principle energy level is slightly further away from the nucleus and can hold a.
The energy of a given atomic orbital is therefore proportional to the inverse square of the principal quantum number. In chemistry the principal energy level of an electron refers to the shell or orbital in which the electron is located relative to the atoms nucleus. In the n1 shell you only find s orbitals in the n2 shell you have s and p orbitals in the n3 shell you have s p and d orbitals and in the n4.
Each energy levels can only accommodate a specific number of electrons. This level is denoted by the principal quantum number n. The energy levels are typically referred to by their shell number rather than their energy level.
Where R H is called Rydberg constant whose value is 21810 18 J. The maximum number of electrons found on energy levels one through six are two eight 18 32 50 and 72. What is Principal Quantum Number N.
The Third Principle Energy Level can hold a maximum of how many Electrons. We call the first energy level after the ground state the first excited state. The number of electrons in each sublevel Electrons fill in energy orderAufbau Principle not energy level order.
The first principle energy level is closest to the nucleus and can hold a mxaimum of two electrons. The succeeding electrons must now occupy the next. For example the 1st principal energy level can only occupy two electrons.
When we consider hydrogenic atoms with nuclear charges greater than one we must allow for the increased attraction between the nucleus and the electron and the resultant change in the energy. The foundation of orbitals chemistry starts with Bohr who established that electron orbitals represent an energy level in terms of their distance from the Nucleus. Electrons if given the chance will fall towards the lowest energy level they can.
The energy level of the bonding orbitals is lower and the energy level of the antibonding orbitals is higher. The first element in a period of the periodic table introduces a new principal energy level. These integers are also known as the principal quantum numbers.
Each Principle Energy Level is comprised of different Sublevels which are. S p d f. These stationary states energy level for an electron are numbered as n 1 2 3.
The fourth principal energy level of an atom has a maximum of 32 electrons. The Principal Energy Level the only holds that of sublevels.
In thermodynamics heat is energy in transfer to or from a thermodynamic system by mechanisms other than thermodynamic work or transfer of matter. Heat energy also known as thermal energy refers to the amount of kinetic energy molecules or atoms have at a certain point in time.
 What Is Heat Energy Thermal Properties Of Matter Basic Physics Msbte Ekeeda Com Youtube
What Is Heat Energy Thermal Properties Of Matter Basic Physics Msbte Ekeeda Com Youtube
Every matter has heat energy.
/heat-energy-definition-and-examples-2698981-final-2-5b76efbcc9e77c005028d736.png)
What is heat energy. Heat is the total energy of these atoms and molecules as they move. Thermal energy is the result of the movement of particles called molecules and atoms. If two bodies at different temperatures are brought together energy is transferredie heat flowsfrom the hotter body to the colder.
Physics a thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the capacity of a physical system to do work. Heat energy can be transferred from one object to another. An object with molecules that are very excited and move around rapidly is known as being hot while an object with molecules whose atoms move around less rapidly is known as cold.
When we touch any material that conducts heat if it has a temperature higher than that of our body we feel warm. The units of energy are joules or ergs. Energy can take a wide variety of forms.
The effect is usually an increase in the temperature of the colder body. Heat energy - a form of energy that is transferred by a difference in temperature. The transfer or flow due to the difference in temperature between the two objects is called heat.
It should also be noted that work and heat are closely related see heat vs work for more information. The various mechanisms of energy transfer that define heat are stated in the next section of this article. Heat is a transfer of thermal energy caused by a difference in temperature.
In other words heat is energy while temperature is a measure of energy. Energy free energy - physics a thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the capacity of a physical system to do work. An objects temperature doesnt tell us how much heat energy it has.
For example an ice cube has heat energy and so does a glass of lemonade. Thermal Energy and Heat Thermal Energy and Heat While thermal energy refers to the total energy of all the molecules within the object heat is the amount of energy flowing from one body to another spontaneously due to their temperature difference. Heat absorbed by a unit mass of a material at its boiling point in order to convert the material into a gas at the same temperature.
Heat energy also called thermal energy is the energy an object has because of the movement of its molecules and heat can be transferred from one object to another object. The units of energy are joules or ergs. The heat is a form of energy that transfers from the higher temperature object to the lower temperature object and is transferred through the conduction the convection and the radiation.
This energy can be transferred from one object to another due to the difference in temperature. The classification of heat is done on this basis as hot and cold. An example of heat energy is boiling water.
Most of us refer the word heat to anything that feels warm but scientifically heat is defined as the flow of energy from a warm to a cooler object. The faster the molecules or atoms are moving the more heat energy they have. Heat is a form of energy that always travels from a hotter substance to a colder substance.
Temperature is a measurement of how hot or cold something is. Heat energy is all around us such as in icebergs volcanoes and our bodies. Heat refers to the transfer of energy between systems or bodies whereas temperature is determined by the energy contained within a singular system or body.
The definition of heat energy is the transfer of energy from one thing to another by kinetic energy usually causing a higher temperature. Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids liquids and gases. Heat and heat energy are terms we use to describe the level of activity for the molecules in an object.
Temperature is a measure of the energy that matter contains or h. Since heat is a movement of energy it is measured in the same units as energy. Its easy to see why not if you think about an iceberg and an ice cube.
Heat is a form of energy but it is energy in transit. This figure shows how the speed of the atoms and molecules. Heat is the energy stored inside something.
Heat energy that is transferred from one body to another as the result of a difference in temperature. If something has many particles moving very rapidly then we would feel that substance as being hot. This temperature difference is also called a temperature gradient.
The faster the atoms and molecules move the higher the temperature. Heat energy on Earth.
Electrical energy is the energy derived from electric potential energy or kinetic energy. In other words electrical energy is the work done by the moving streams of the electrons or charges.
 Electrical Energy Energy Education
Electrical Energy Energy Education
A typical nuclear power plant has an electric-generating capacity of 1000 MWe.

What is electrical energy. Electricity is the flow of electrons. The heat source in the nuclear power plant is a nuclear reactor. In other words charged particles create.
When 1 KW load is operated for one hour it extraction 1 kWh of energy. It carries electricity from the transmission system to individual consumers. For example electrical energy is transferred to the surroundings by the lamp as light energy and thermal heat energy.
In other words charged particles create electric fields that exert pressure on other charged particles within the field. The name is a bit of a misnomer though because electrical energy itself often called electricity isnt really a form of energy. Electricity is the set of phenomena caused by the existence interaction and motion of electric charges.
This form of energy manifests itself in charged particles movement on the surface of a conductive material. If current i ampere flows through a conductor or through any other conductive element of potential difference v volts across it for time t second the electric energy is Electrical Energy Formula. We define electricity as the form of energy that results from the existence of a potential difference between two points.
Electrical energy can be defined as the power consumed for a particular period. Electrical energy is energy derived from electric potential energy or kinetic energyWhen used loosely electrical energy refers to energy that has been converted from electric potential energy. The world is made of matter.
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electric power. Electrical energy is the energy derived from electric potential energy or kinetic energy of the charged particles. Electrical energy is energy thats stored in charged particles within an electric field.
All matter is made up of atoms and an atom has a center called a nucleus. In general it is referred to as the energy that has been converted from electric potential energy. Its more a way that energy is transferred between objects.
In other words a form of energy derived and converted from kinetic energy or electrical potential energy. Electric energy is the energy created by electrons moving through an electrical conductor. Such energy could either be kinetic energy or potential energy.
Considered a circuit shown in the figure below. It is the energy derived from electric potential energy or kinetic energy. A battery transfers stored chemical energy as charged particles called electrons typically moving through a wire.
It produces 1 000 000 000 joules of electrical energy per second. Electrical energy is a type of energy caused by the movement of charge or electrons. The expression of electric power is The electrical energy is.
All matter contains atoms that contain electrons that are always moving. Electric fields are simply areas surrounding a charged particle. Electric energy is unrivaled for many uses as for lighting computer operation motive power and entertainment applications.
Electrical energy is a kind of energy that is derived from the movement of electric charge. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 35 kV with the use of transformers. When the electric charges are continuously flowing electrical energy becomes a form of kinetic energy.
Electric energy is the movement of electronsIt can also be called electricity. When these two points are brought into contact by an electrical conductor like a copper wire we obtain an electric current. Electric fields are simply the field around charged particles.
When electrons are forced down a conductive path such as a wire the movement produces electricity or electric energy. Unit of Electrical Energy. The faster the movement of charges the more the energy they carry.
The main component of the economic development of a country is energy. Electrical energy is a type of kinetic energy because of the movement of charge from one point to another. Electric power energy generated through the conversion of other forms of energy such as mechanical thermal or chemical energy.
The one-kilowatt hour is the total energy consumed. Primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage power to. This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electric potential that is delivered by an electrical circuit eg provided by an electric power utility.
Lightning is one good example of electrical energy in nature so powerful that it is not confined to a wire. Electrical energy is the work done by electric charge. It is measured in terms of a kilowatt-hour.
Electrical energy is the energy energy stored in charged particles in the electric field. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The charged particles can be electrons protons or ions.
We can define electrical energy as the energy generated by the movement of electrons from one point to another. Electrical energy is the form of kinetic energy because it produces by the movement of the electrical charges. Electricity is a form of energy.