Photo 12Getty Images Bohrs model of 1913 for the hydrogen atom had circular electron orbits about the proton like Earth orbits around the sun says Herschbach. Bohrs theory of atomic model was quite successful in explaining the stability of the atom and the line spectrum of a hydrogen atom.
Bohr Model Of The Atom Overview And Examples
The Bohr model of the atom is often called the planetary model.
In the bohr model of the atom. He modified the problems and limitations associated with Rutherfords model of an atom. This video looks at the pioneering work of Niels Bohr who proposed a novel model of the atom in 1913 which would lay the foundations for a quantum mechanical. 309 pm Highest tides occur when the sun moon and earth are in alignment.
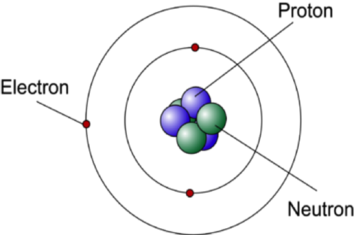
Bohrs Model Of An Atom 1An atom is made up of three particleselectronsprotons and neutronsElectrons have negative chargeprotons have positive charge whereas neutrons have no chargeDue the presence of equal number of negative electrons and positive protonsthe atom on the whole is electrically neutral. The Bohr model depicts the atom as a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus similar in structure to the solar system but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. Overview of the Bohr Model Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr Model of the Atom in 1915.
Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Bohr combined classical and quantum mechanical theories to explain the structure of atom and the revolving electronsBohrs p. A Danish physicist named Neil Bohr in 1913 proposed the Bohr atomic model. There were various related with the atomic structure and some of them are Rutherford model and Bohr model.
The Bohr Model has an atom consisting of a small positively charged nucleus orbited by negatively charged electrons. As shown in Figure 1 for a hydrogen atom the Bohr model envisions the nucleus of the atom occupying a fixed position at the center of an atomic system with the electron revolving around the nucleus in the same way that a planet revolves around the sun. Earlier in Rutherford Model Rutherford explained in an atom a nucleus is positively charged and is surrounded by electrons negatively charged particles.
Niels Henrik Bohr 1885-1962 was a Danish physicist who developed the atomic model and won the 1922 Nobel prize in physics. Solution for In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom in the lowest energy state the electron orbits the proton at a speed of 22 x 106 ms in a circular orbit. The Bohr atomic model theory made right predictions for lesser sized atoms like hydrogen but poor phantom predictions are obtained when better atoms are measured.
Atoms absorb or emit radiation only. Different atomic models help in analyzing the structure of atom properly. For example a Bohr diagram of the element boron shows five protons and five electrons.
Bohr model description of the structure of atoms especially that of hydrogen proposed 1913 by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr. A regular atom has all of its electrons in the ground state When electrons absorb energy they become excited and go to higher energy levels When these excited electrons drop to lower energy levels they release energy in the form of photons Each specific photon relates to a specific colour based on the energy it carries Failures of the Bohr Model The energy level values were only accurate. The Bohr model of the atom a radical departure from earlier classical descriptions was the first that incorporated quantum theory and was the predecessor of wholly quantum-mechanical models.
The Bohr model and all of its successors describe the properties of atomic electrons in terms of a set of allowed possible values. Bohrs Atomic Model A Danish physicist called Neil Bohr 1913 proposed the Bohr atomic model. Heres a closer look at the Bohr Model which is sometimes called the Rutherford-Bohr Model.
The areas within this plane will have the highest tides while those 90 degrees to the pla. Two electrons orbit the. The Bohr model of the boron atom has a nucleus in the center and two energy levels also known as shells or orbitals around the outside.
As a theory it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. The Bohr model was an improvement on the earlier cubic design 1902 the plum-pudding model 1904 the Saturnian model 1904 and the Rutherford model 1911. The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom compared to the valence shell atom model.